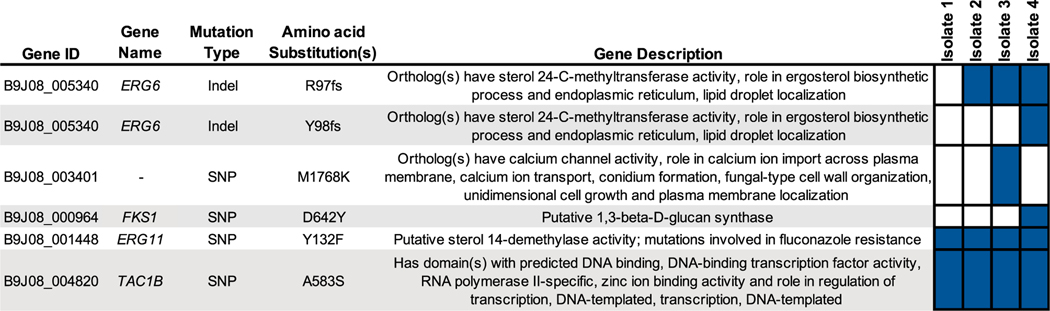
Fig. 2.
Whole genome sequencing reveals an association between mutations in Candida auris ERG6 and high-level amphotericin B resistance. Non-synonymous mutations differing between C. auris clinical isolates in this study, and those previously associated with antifungal resistance are shown with gene identifier, gene name, mutation type, encoded amino acid substitution(s) and gene description (as listed on the Candida Genome Database; candidagenome.org). Boxes filled in blue indicate the presence of the listed mutation in the corresponding clinical isolate. Isolate 4 possesses both the R97 fs and Y98 fs mutations in ERG6, resulting in the allele containing the amino acid substitutions RYY97LVS in the native reading frame.