Figure 3.
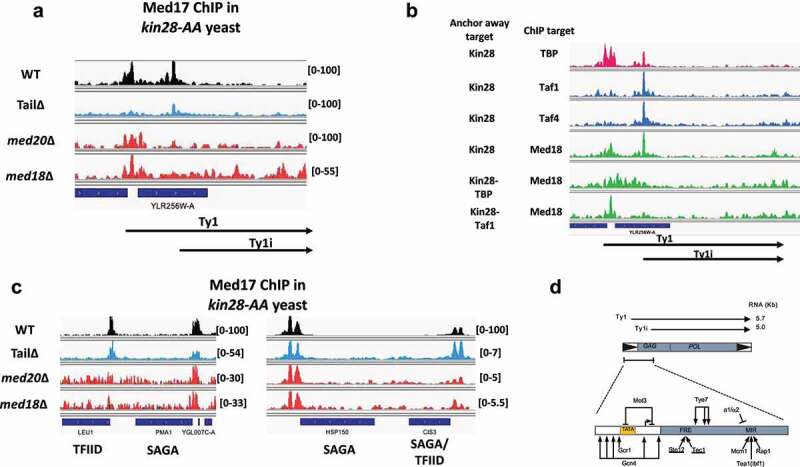
Opposing effects of deletion of mediator tail and head module subunits on mediator association with Ty1 and Ty1i promoters. (a) Med17 (head) ChIP-seq reads mapped to YLRWTy1-3 in wild type, med2∆ med3∆ med15∆, med18∆, and med20∆ yeast. Transcripts corresponding to Ty1 and Ty1i are indicated below. Note that reads cannot be unambiguously assigned to individual Ty1 elements; hence, YLRWTy1-3 serves as a proxy for a “representative” Ty1 element. Relative scales per total number of mapped reads are indicated. Data is from [31,55]. (b) ChIP-seq reads for TBP, Taf1 and Taf4 (TFIID subunits), and Med18 (head) mapped to YLRWTy1-3 with depletion of Kin28, Kin28 and TBP, or Kin28 and Taf1, as indicated. Data is from [31,88]. (c) Browser scans showing Med17 (head) occupancy at LEU1, PMA1, HSP150, and CIS3 in wild type, med2∆ med3∆ med15∆, med18∆, and med20∆ yeast after Kin28 depletion. Designation of genes as SAGA-dominated or TFIID-dominated is from [46]. Relative scales per total number of mapped reads are indicated. Data is from [31,55]. (d) Schematic diagram of Ty1. Ty1 and Ty1i transcripts are indicated at the top; expanded view at bottom indicates binding sites for the indicated TFs [52].
