Figure 6.
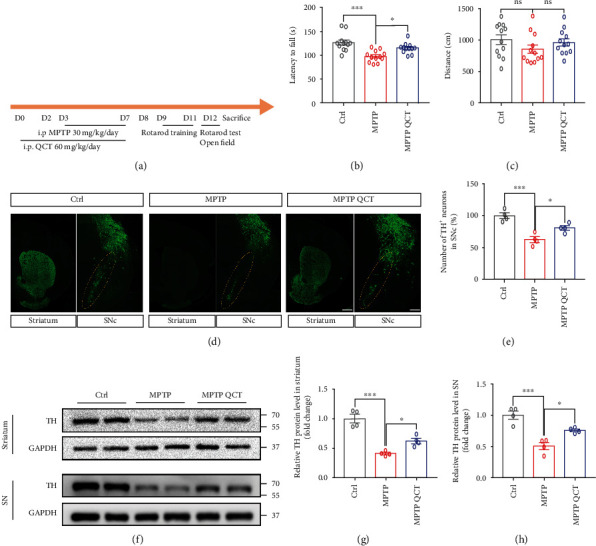
QCT attenuated behavioral disorders and protected the dopaminergic neurons in PD mouse models. (a) Diagram of the experimental procedure. Mice were intraperitoneally (i.p.) injected with MPTP (30 mg/kg/day) or saline for 5 consecutive days. Three days before treatment with MPTP, mice received QCT (60 mg/kg/day, i.p.) treatment. All animals were trained for 3 days and tested on day 12. (b) Rotarod tests were conducted for Ctrl, MPTP, and MPTP QCT groups (n = 12). (c) Open field test was conducted for Ctrl, MPTP, and MPTP QCT groups (n = 12). (d) Representative immunofluorescent staining of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) in the substantia nigra compacta (SNc) and striatum. Scale bar = 200 μm. (e) Quantification of relative TH-neurons in SNc (n = 4). (f) Representative immunoblots of the TH protein in SN and striatum. (g, h) Quantification of TH protein levels in SNc and striatum (n = 4). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ns: no significant difference.
