Figure 2.
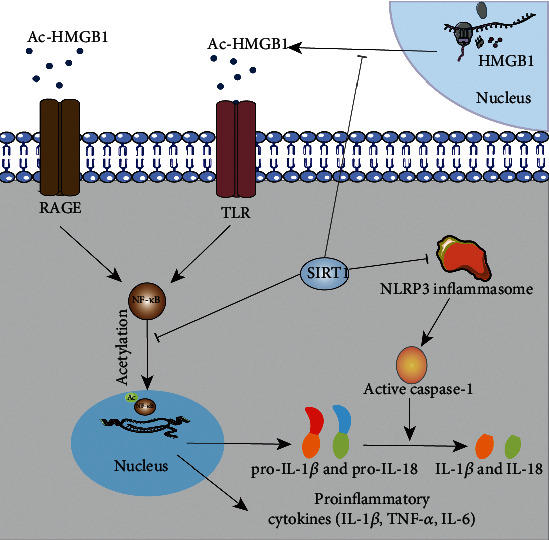
The signal pathway of SIRT1-mediated anti-inflammatory in stroke. The picture shows the signal pathway of SIRT1-mediated anti-inflammatory in stroke. SIRT1 can inhibit the production of proinflammatory factors through the deacetylation of HMGB1, NF-κB, and NLRP3 inflammasome, thus achieving an anti-neuroinflammatory effect. Through the deacetylation of HMGB1 and NF-κB, the synthesis of some proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in the nucleus was inhibited. In addition, through the deacetylation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, the function of caspase-1 was restricted, and eventually, the pathway of conversion of pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 to IL-1β and IL-18 was blocked.
