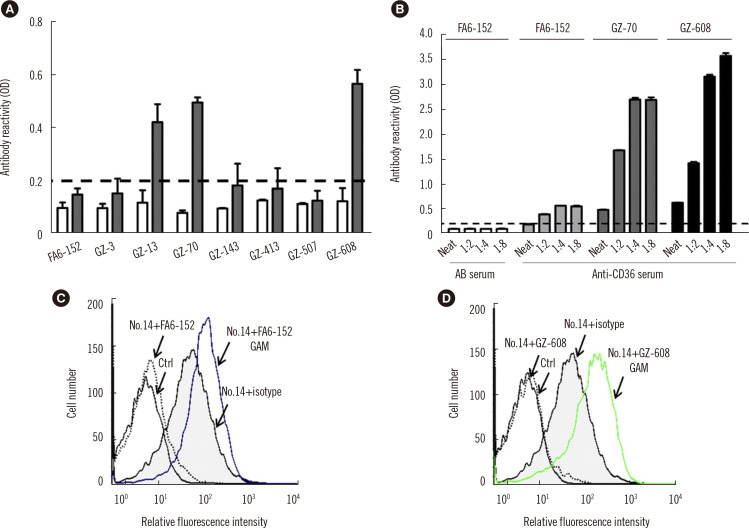
Fig. 2.
Characteristics of anti-CD36 serum in MAIPA and binding assays using different capture mAbs. (A) Platelets were first incubated with anti-CD36 serum (serum number 8, gray columns) and AB serum (white columns) and then with eight anti-CD36 mAbs (20 μg/mL) as indicated and analyzed using the MAIPA assay. (B) Platelets were incubated with anti-CD36 serum at different dilutions (neat, 1:2, 1:4, and 1:8) and the anti-CD36 mAbs FA6-152, GZ-70, and GZ-608 (20 μg/mL), as indicated. The cut-off for each assay was determined by analyzing AB sera from healthy blood donors (N=8, white columns). The reaction was considered positive when the result was >0.200 (cut-off; mean value±3 SDs; N=8; dotted line). (C, D) Effects of the mAbs FA6-152 and GZ-608 on the binding of serum number 14 to CD36+ platelets as determined using flow cytometry. “Isotype” stands for mouse IgG1, “Ctrl” for AB serum+mAb, and “GAM” for fluorescence-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG antibody.
Abbreviations: OD, optical density; MAIPA, monoclonal antibody immobilization of platelet antigens; mAbs, monoclonal antibodies.