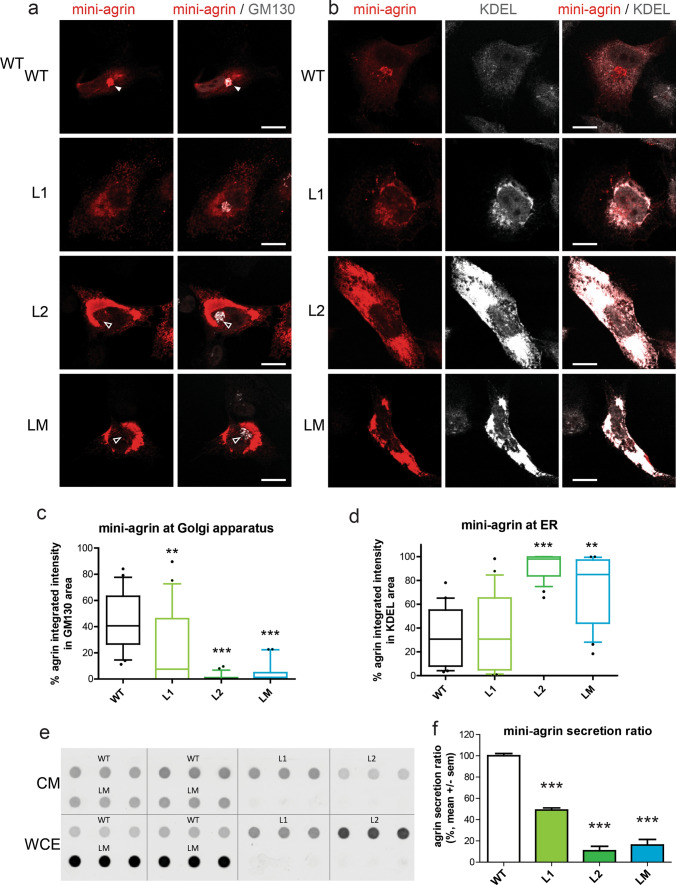
Fig. 4.
Mutant mini-agrins accumulate in the endoplasmic reticulum and are less secreted. a Confocal images of SHEP cells transfected with agrin IRES eGFP (green) counterstained for agrin (red) and Golgi apparatus (GM130, white). Full white arrowheads show agrin enrichment at the Golgi apparatus. Empty white arrowheads indicate the absence of agrin in the Golgi apparatus. Scale bar: 10 μm. b Confocal images of SHEP cells transfected with agrin IRES eGFP counterstained for agrin and an endoplasmic reticulum marker KDEL (white). Scale bar: 10 μm. c, d Quantification of agrin/Golgi co-localization and agrin/endoplasmic reticulum (ER) co-localization (Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn's multiple comparison test; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). e Representative dot-blot for agrin quantification in conditioned medium (CM) and whole-cell extract (WCE) from cultures expressing WT, L1, L2 or LM mini-agrins. f Graphic representation of the ratio of secreted agrin quantified from the dot-blots and at least three independent experiments (one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test; ***p < 0.001)