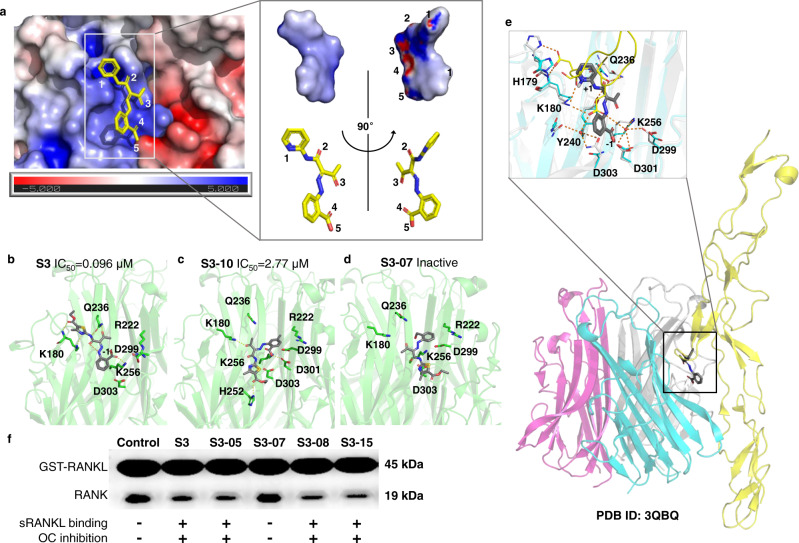
Fig. 5. Molecular basis of selective sRANKL inhibition.
a Binding model of S3-15 and sRANKL: The binding site is formed at the intersection of two sRANKL monomers that are attracted by opposite static charges (blue: positive charge; red: negative charge). S3-15 resides at the positively charged region due to S3-15 is a negatively charged molecule (the partially negative charged atoms are labeled with 1∼5). The partial changed surface was calculated with Adaptive Poisson-Boltzmann Solver (APBS) electrostatics method. b–d Represent three binding models of S3-sRANKL, S3-10-sRANKL, S3-07-sRANKL. Their binding powers are in descending order. Correspondingly, their osteoclastogenesis inhibitory activities are also in descending order. e The binding complex of S3-15-RANKL-RANK was built based on (PDB ID: 3QBQ). This model shows that S3-15 is right in the middle of RANKL (colored in cyan) and RANK (colored in yellow) and blocks the binding of RANKL and RANK. The residues surrounding S3-15 are the key residues for RANKL and RANK binding. f GST pull-down experimental results show that S3 derivatives (S3, S3-05, S3-07, S3-08, and S3-15) disturb RANKL-RANK interaction leading to OC inhibition by binding to sRANKL.