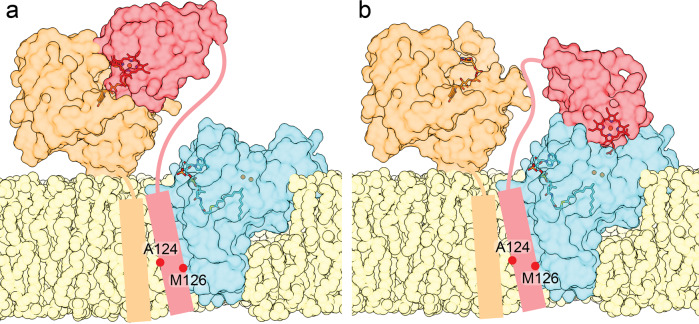
Fig. 7. Model of the stable SCD1-cyt b5-b5R complex.
SCD1 (cyan), cyt b5 (red), and b5R (orange) are shown as translucent surfaces highlighting the diiron center (orange sphere) and acyl-CoA (cyan stick) in SCD1, heme (deep red stick) in cyt b5, and FAD (brown stick) in b5R. SCD1 forms a complex with the TM helix of cyt b5 and b5R in lipid bilayer (yellow). The relative positions of two residues on the TM helix of cyt b5 are marked. A flexible linker connecting the soluble domain of cyt b5 and b5R to their TM helix allows the transition of two states: a cyt b5 receiving an electron from b5R; and b cyt b5 delivering an electron to SCD1.