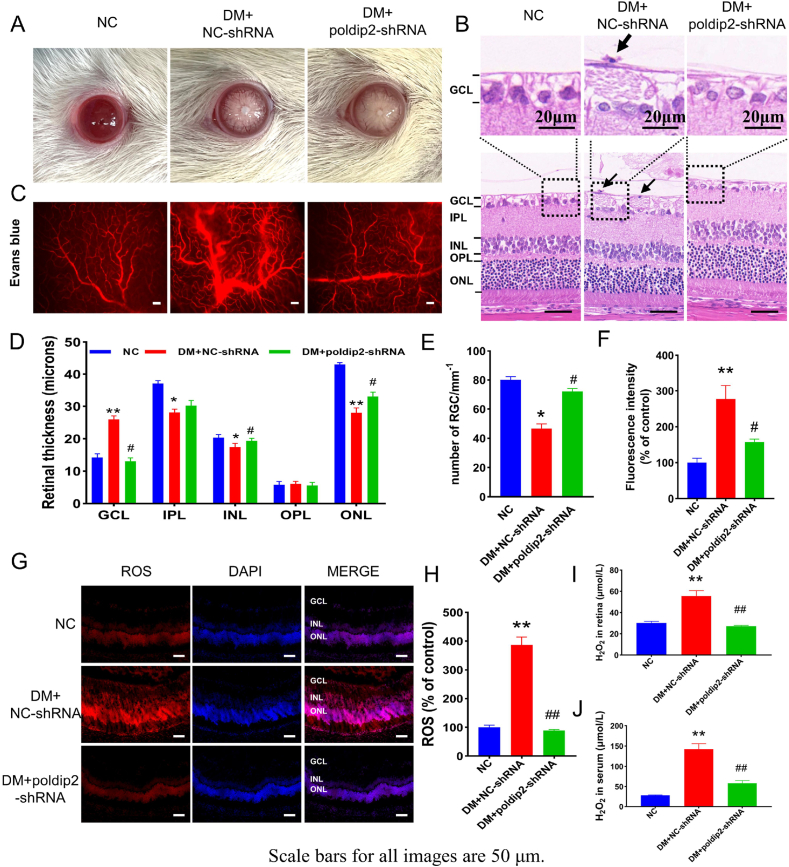
Fig. 8.
Knockdown of poldip2 in vivo improves the pathological changes of DR and reduces ROS. (A) Photographs of the ocular surface of rats in different groups. (B) Photographs of the HE staining of rat subretinal tissues in different groups. (C) Photographs of Evans blue angiography of rat retina in different groups with/without poldip2-shRNA treatment. (D) Analysis of the thickness of the rat subretinal layers. (E) The number of retinal ganglion cells. (F) Analysis of the fluorescence intensity. (G–H) The levels of ROS in rat retina in different groups with/without poldip2-shRNA treatment. (I–J) The levels of H2O2 in rat retina in different groups with/without poldip2-shRNA treatment. One-way ANOVA. Data are the means ± SEM, n = 3–4/group, scale bar: 50 μm. Compared with NC group: **p < 0.01; Compared with DM + NC-shRNA group: #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01. NC: normal control group. DM + NC-shRNA group: diabetic group treated with scrambled-AAV9-shRNA. DM + poldip2-shRNA: diabetic treated with AAV9-poldip2-shRNA. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)