Fig. 6.
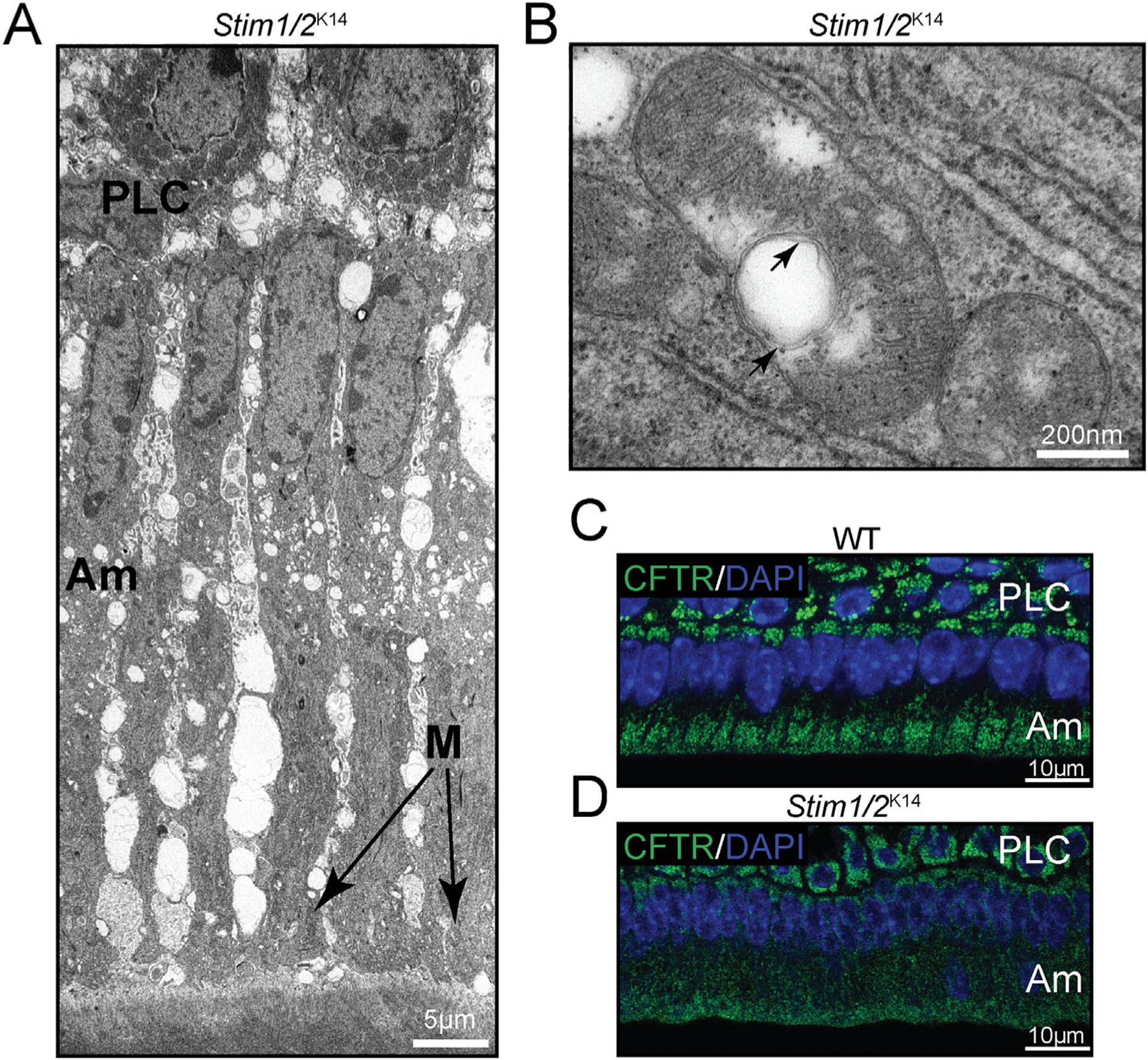
Stim1/2-deficient ameloblasts. (A) TEM micrograph of Stim1/2-deficient maturation stage ameloblasts (Am) showing arrested development of the ruffled-border, increased intercellular space, and apically placed mitochondria. These characteristics are atypical of ruffled-ended ameloblasts but define smooth-ended ameloblasts. Stim1/2-deficient ameloblasts analyzed in different positions of the lower incisors all showed a smooth-ended morphology, suggesting that Ca2+ signals are important for the formation of the ruffled-border. (B) Mitochondria of Stim1/2-deficient mice commonly showed white (non-electron dense) bodies with multiple outer membranes in their matrix. (C–D) The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) protein is important in chloride transport during enamel maturation. CFTR is a key target of S-glutathionylation. In WT ameloblasts, CFTR is localized at the apical side of the ameloblasts as shown by the immunofluorescence analysis of WT ameloblasts (C), but in Stim1/2-deficient ameloblasts, CFTR is mislocalized (D), suggesting that it was not S-glutathionylated. DAPI staining (blue) was used to indicate cell nuclei.
