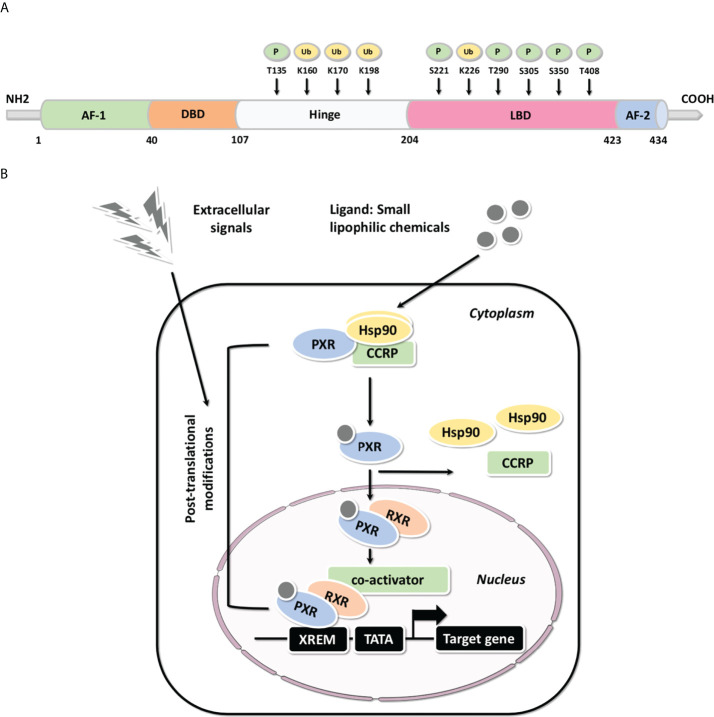
Figure 2.
The structure and molecular mechanisms associated with PXR (A) Common structure of metabolic nuclear receptor and the post-translational modifications of PXR protein structure. The domain structure of metabolic nuclear receptor is presented, including the typical N-terminal non-ligand-dependent AF-1, a highly conserved DBD, a less conserved hinge region, a C-terminal LBD and AF-2; PXR may be modified by phosphorylation and ubiquitination through protein-protein interactions, thus, reported phosphorylation and ubiquitination are highlighted (P: Phosphorylation; Ub: Ubiquitination). (B) The molecular mechanisms of PXR-mediated gene activation: Molecular analysis based on both in vivo and in vitro models have systematically illustrated the mechanism of PXR activation.