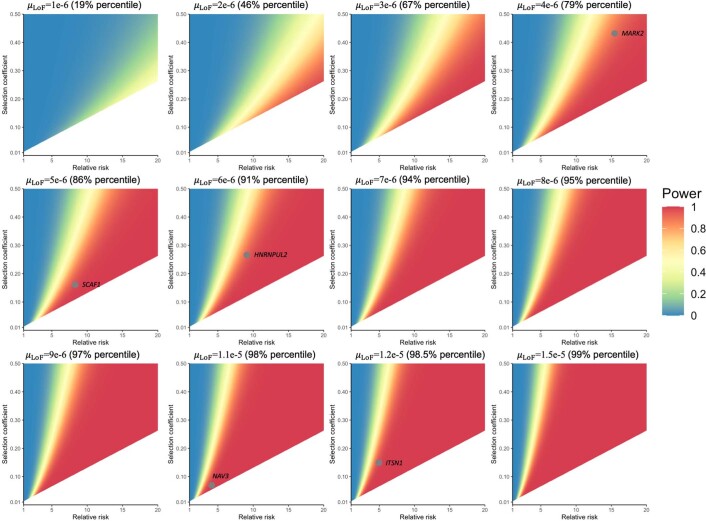
Extended Data Fig. 6. Power of case-control association by rare LoFs variants (‘mega-analysis’) with sample size equal to current study.
The mega-analysis of current study compares the rate of LoF variants in 32,024 unrelated ASD cases with population controls with sample sizes about 76,000~132,000. For power calculation, we assumed that population controls are infinite so that cumulative allele frequency are known and presumed to be at equilibrium under selection-mutation balance for constrained genes (f = μLoF/s). Experiment-wide error rate was set at 9e-6 (0.05 divided by the number of autosomal genes at gnomAD LOEUF 30%). Power is calculated as a function of relative risk for ASD (RR) and selection coefficient (s) across different haploid LoF mutation rates (μLoF) using an analytic approximation by Zuk et al.41. We only considered selection coefficient between 0.01 and 0.5 and relative risk to ASD between 1 and 20, because genes with huge effect sizes and larger selection coefficients are expected to be identified from the enrichment of de novo variants. The triangular region where s < 0.013RR are left blank because the parameters in this region are not compatible with the current estimates of prevalence of ASD (1/54)71 and sex-averaged reduction of reproductive fitness (0.71)72. Five new ASD genes identified in this study are placed onto the heatmap closest to its LoF mutation rate. Their positions within heatmaps are taken from point estimates of using gnomAD exomes (non-neuro subset) as population controls.