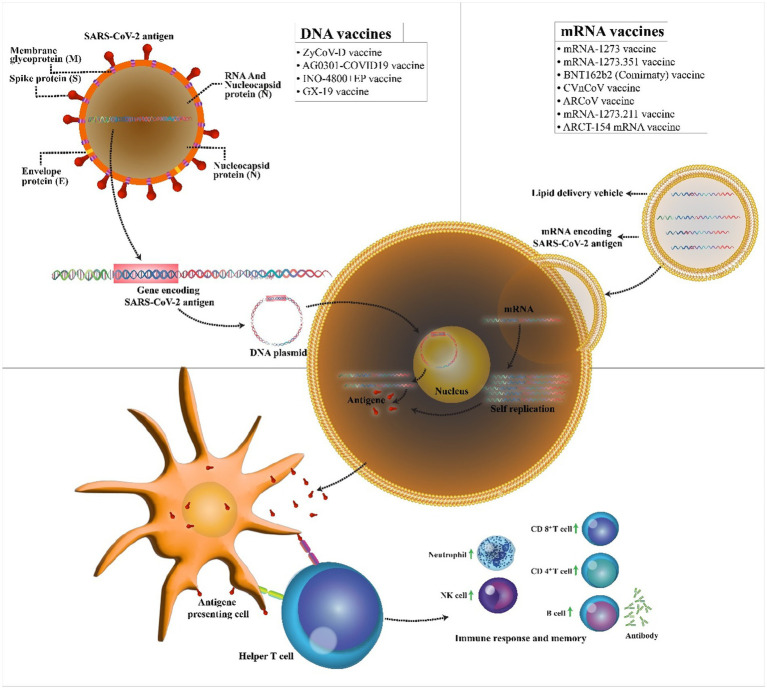
Figure 2.
Mechanism of action of the COVID-19 DNA and RNA vaccines. COVID-19 mRNA vaccine has strands of messenger RNA inside a coating that protects it from enzymes. COVID-19 DNA vaccine comprises a plasmid that after the vaccine reaches the nucleus, it must be transcripted to an mRNA. In both vaccines, mRNA is translated into the human cells. Next, the encoded protein is expressed in the host cells, and the SARS-CoV-2 antigen can be then presented to antigen-presenting cells. Then, T helper cells stimulate the immune responses including an increase in neutrophils, NK cells, CD 4+ T cells, CD 8+ T cells, and B cells.