FIGURE 2.
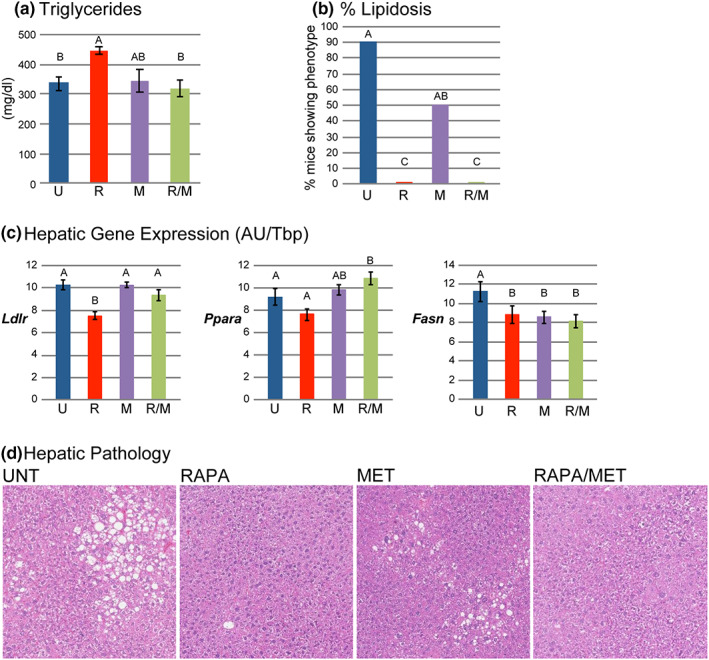
RAPA/MET‐treatment prevented RAPA‐mediated elevation of triglycerides. RAPA‐ and RAPA/MET‐treatments prevented hepatic lipidosis. (a) RAPA‐treatment increased plasma triglyceride level, but combination with MET blocked this effect. (b) Reduction of hepatic lipidosis was suggested in MET‐treated mice; hepatic lipidosis was completely prevented in RAPA‐ and RAPA/MET‐treated mice (nominal logistic fit, likelihood ratio test for presence of lipidosis: overall, p < 0.0001; post hoc pairwise tests: UNT vs MET, p = 0.06; UNT vs RAPA or RAPA/MET, p < 0.0001). (c) RAPA‐treatment reduced hepatic Ldlr and Ppara expression; co‐treatment with MET blocked the reduction of Ldlr expression and increased Ppara expression consistent with triglyceride levels. All 3 treatments reduced expression of Fasn. (d) Representative histology of moderate hepatic lipidosis in UNT mice, mild hepatic lipidosis in MET‐treated mice, and absence of hepatic lipidosis in RAPA‐ and RAPA/MET‐treated mice. Mean ± SE. N = 6–8 mice per treatment for triglycerides and 9–10 per treatment for gene expression. Significance annotations and treatment abbreviations as in Figure 1
