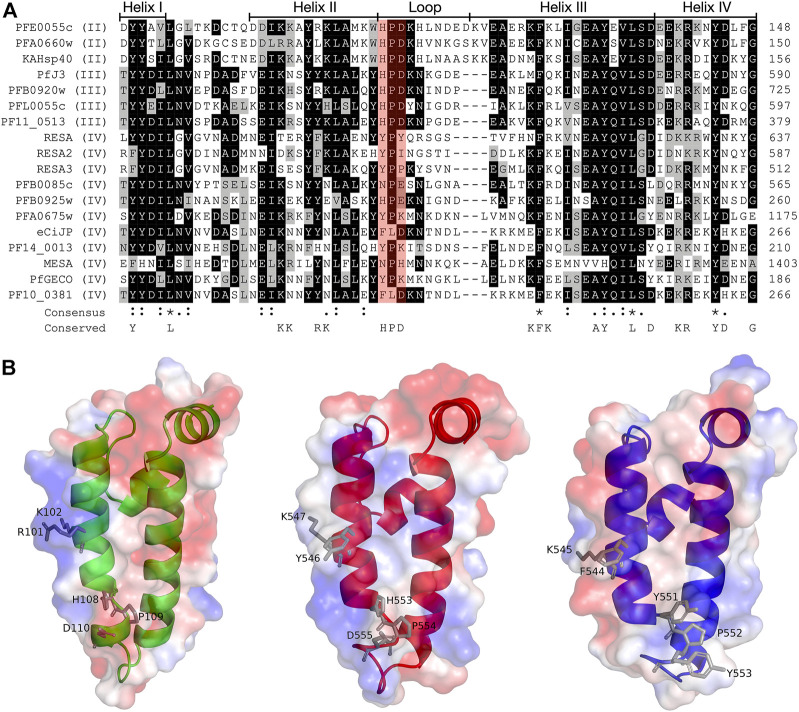
FIGURE 2.
Multiple sequence alignment and molecular modelling of the J domains of exported PfJDPs. (A) Multiple sequence alignment of the J domains of the 18 exported PfJDPs proteins. The proteins are defined by either their PlasmoDB accession number or common name in the first column, and the roman numerals in brackets refer to the type of JDP. Colored in black are identical amino acids (in at least 50% of the aligned sequences), colored in light grey are similar amino acids (in at least 50% of the aligned sequences), and colored in white are the amino acids with no identity or similarity. The default categories for similar amino acids were applied to the multiple sequence alignment (ILV, FWY, KRH, DE, GAS, P, C and TNQM). The row titled “Consensus” are the common consensus symbols of the multiple sequence alignment: an * (asterisk) indicates positions which have a single, fully conserved residue; a: (colon) indicates conservation between groups of strongly similar properties; and a. (period) indicates conservation between groups of weakly similar properties. The row titled “Conserved” refers to residues previously found to be highly conserved across J domains of different origins, with the residues defined at the bottom of the alignment (Hennessy et al., 2000; Hennessy et al., 2005). The protein helices and loop region are defined by bidirectional lines on top of the alignment. Highlighted in red shading is the HPD motif. The alignment was created using Clustal Omega (Sievers and Higgins, 2018) and rendered with box shading using Multiple Align Show (Stothard, 2000). (B) Three dimensional models of the J domains of PFE0055c type II (green), PfJ3 type III (red), and RESA type IV (blue) to illustrate the conserved HPD and RK motif (grey sticks). The positive charge is shown in blue colored surface, the negative charge is shown in red colored surface and the neutral potential are shown in white colored surface. The surface electrostatic potential was calculated by APBS. The models were prepared using SWISS-MODEL (Waterhouse et al., 2018; the template structures are listed in Supplementary Table S1) and graphically rendered using PyMol 2.5.2 (PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.0 Schrödinger, LLC).