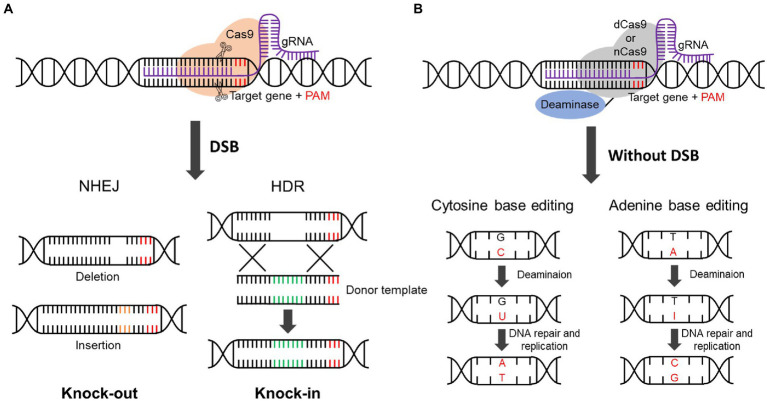
Figure 2.
CRISPR/Cas9 and base editing mechanism. (A) Repair mechanism of CRISPR/Cas9. CRISPR/Cas9 is composed of Cas9 protein and gRNA. Cas9 recognizes the PAM sequence and cleaves 3 bp upstream of PAM to cause the DSB. When a DSB occurs, the cellular repair mechanism, including NHEJ and HDR processes, is initiated. NHEJ causes deletion or insertion, resulting in gene knockout due to a frameshift change. The donor template is inserted by HDR, and knockin occurs. DSB, Double-strand break; NHEJ, non-homologous end joining; HDR, homology-directed repair; PAM, protospacer adjacent motif. (B) Mechanism of base editing. The cytosine base editor or adenine base editor is made up of dead Cas9 (dCas9) or nickase Cas9 (nCas9) fused with cytosine deaminase or adenine deaminase. Cytosine deaminase removes the amine group from cytosine, resulting in a U-G mismatch. The U-G pair is converted to T-A by DNA repair and DNA replication. Adenine deaminase converts adenine to inosine by removing the amine group, resulting in an I-T mismatch. The I-T pair is converted to G-C by DNA repair and DNA replication.