FIGURE 2.
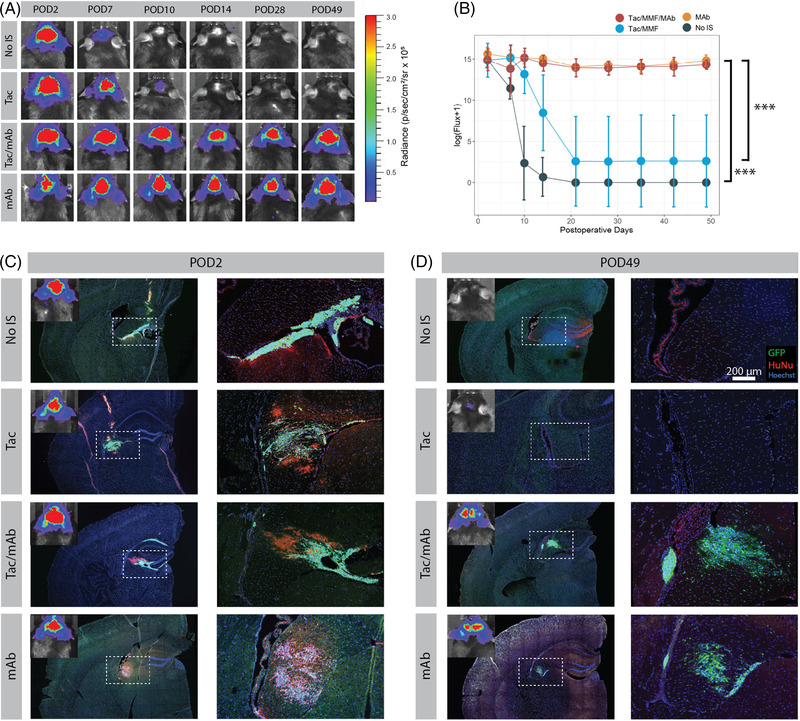
Assessment of immunosuppression protocols using bioluminescent imaging (BLI) to track transplanted hNSC graft survival. (A) Serial BLI detection of transplanted hNSC‐luc+/green fluorescent protein (GFP)+ in C57BL/6J mice (3.6 × 105 total cells) receiving no immunosuppression (No IS), tacrolimus with mycophenolate mofetil (Tac/MMF), Tac/MMF in combination with mAbs against CD40L and CD4 (Tac/MMF/mAbs) or only mAb against CD40L and CD4 (mAbs). (B) BLI signal quantification for all mice at all‐time points demonstrates significant maintenance of BLI signal in mAb treated groups versus Tac/MMF alone or non‐immunosuppressed groups. (C and D) immunohistochemical (IHC) images showing GFP+ grafts (green) colocalized with HuNu (red) in the fimbria fornix target area at POD 2 and POD 49 (endpoint). Starting sample size: n = 10 in No IS group, n = 12 in all other groups. Subsets were euthanized for IHC at POD2 (2 from No IS group and 3 from all other groups) and POD10 (2 from No IS group and 3 from all other groups, IHC data not shown). Remaining animals were used for each BLI data point until study end (POD 49). Data presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) for repeated BLI measures, analysed by linear mixed effects model, ***p < .001. HuNu, human nuclei; IS, immunosuppression; POD, post‐operative day
