FIGURE 7.
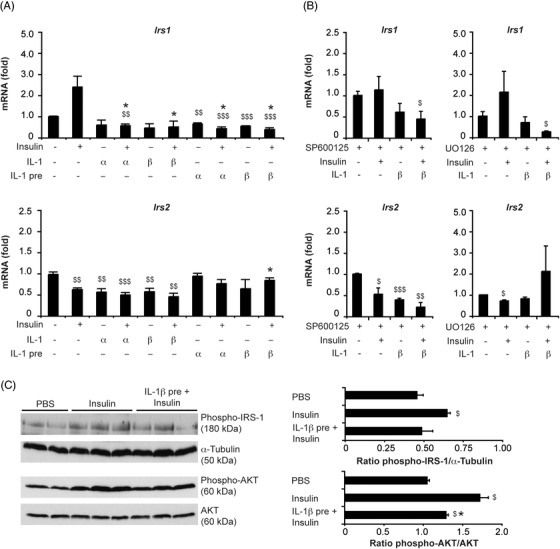
IL‐1 signals alter the expression of IRS‐1 and IRS‐2 in primary hepatocytes and interfere with hepatic insulin signalling in vivo. Relative mRNA expression of IRS‐1 and IRS‐2 in primary WT hepatocytes (A) following ex vivo 3‐h‐stimulation with insulin (100 nM) in the absence or presence of rmIL‐1α/β (10 ng/ml) or after 18‐h‐pretreatment with rmIL‐1α/β (10 ng/ml, IL‐1 pre). (B) To examine the involvement of MAPK pathways in mediating IL‐1‐induced effects, the JNK inhibitor SP600125 (100 μM) or the ERK1/2 inhibitor UO126 (50 μM) was added to hepatocyte cultures 1 h prior to 3‐h‐stimulation with insulin ± rmIL‐1β. (C) Hepatic activation of IRS‐1 (phosphorylation at Ser302) and AKT (phosphorylation at Ser473) was evaluated in 8‐week‐old, male WT mice either treated with vehicle (PBS) or insulin (1.5 U/kg body weight insulin i.p.) at 10 min by Western blot analysis in whole liver tissue lysates. If indicated, rmIL‐1β protein (1 μg i.p.) was administered 30 min before the insulin injection. Data in A and B represent mean of three, respectively, two independent experiments performed in duplicate ± SEM. In C, representative immunoblots with densitometric analysis of three independent experiments are shown. *p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001 for insulin alone vs. insulin + rmIL‐1α/β and $ p < .05, $$ p < .01, $$$ p < .001 for untreated versus treated using unpaired, two‐tailed Student's t‐test (A‐C)
