FIGURE 4.
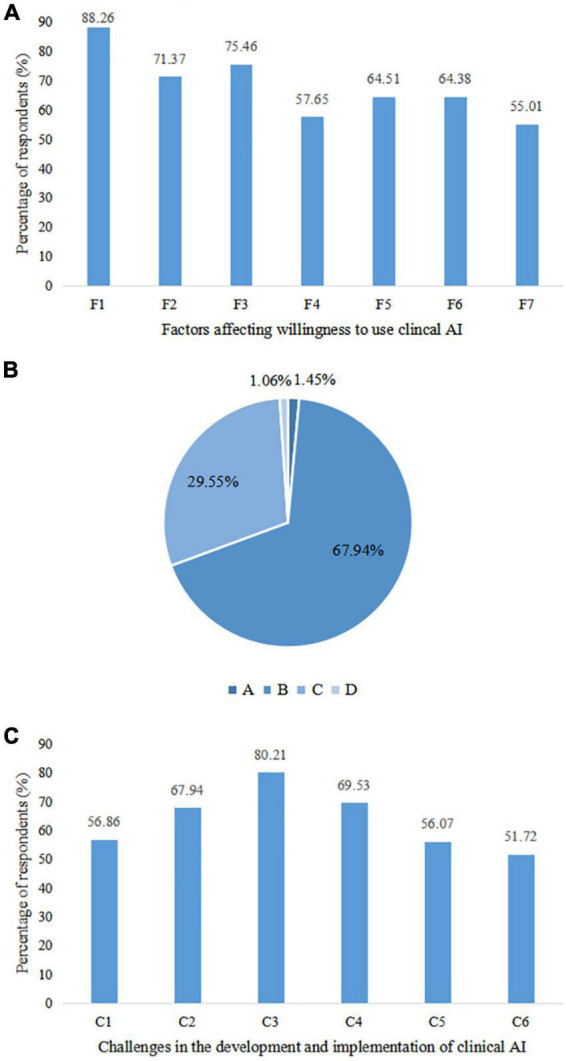
Factors related to use willingness, perceived relationship between physicians and artificial intelligence (AI), and challenges faced by clinical artificial intelligence (AI). (A) Factors associated with willingness to use clinical AI. F1: Accuracy; F2: Efficiency; F3: Ease of use; F4: Widely adopted; F5: Cost-effectiveness; F6: Interpretability; F7: Privacy protection capability. (B) Perceived relationship between physicians and clinical AI. A: Physicians don’t need to use clinical AI; B: Physicians lead the diagnosis and treatment process while clinical AI only plays an auxiliary role; C: Clinical AI completes the diagnosis and treatment process independently under the supervision and optimization of physicians; D: Clinical AI completely replaces physicians for diagnosis and treatment. (C) Challenges to be overcome in the development and implementation of clinical AI. C1: Inadequate algorithms and computational power of clinical AI; C2: Lack of high-quality data for clinical AI training; C3: Lack of inter-disciplinary talents with both medical and AI knowledge; C4: Lack of regulatory standards; C5: Difficulties in integrating clinical AI with existing medical process; C6: Insufficient understanding and acceptance of clinical AI among physicians and medical students.
