Figure 1.
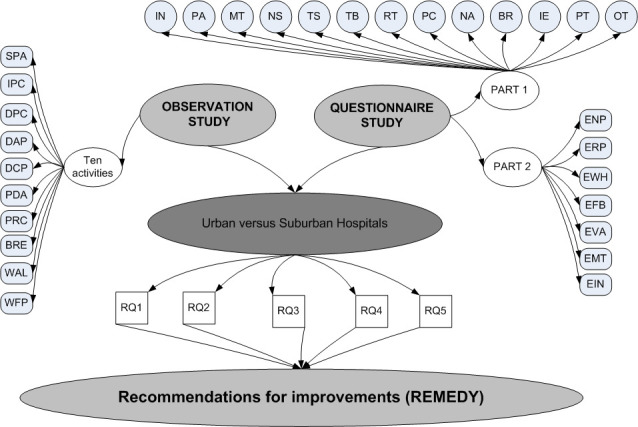
Scheme of study. BR, breaks; BRE, breaks; DPC, direct patient care; DAP, documentation and prescribing; DCP, direct communication with patients; ENP, effect of number of patients; ERP, effect of relevant patients; EWH, effect of working hours; EFB, effect of frequent breaks; EVA, effect of visual and auditory distractions; EMT, effect of multitasking; EIN, effect of interruptions; IN, interruptions; IE, information exchange; IPC, indirect patient care; MT, multitasking; NS, personal/social activities in night shifts; OT, overtime; PA, patient care; PC, professional communication; PT, social and personal task; PDA, patient data analysis; PRC, professional communication; RT, resumption of primary task; S, task switching; SPA, social and personal activity; TPC, professional communication; TB, task break-in; WAL, walking; WFP, waiting for patients’ diagnosis results or colleagues.
