Figure 5. Identification of Hydrophobic Amino Acids Supporting the Secretion of HPs.
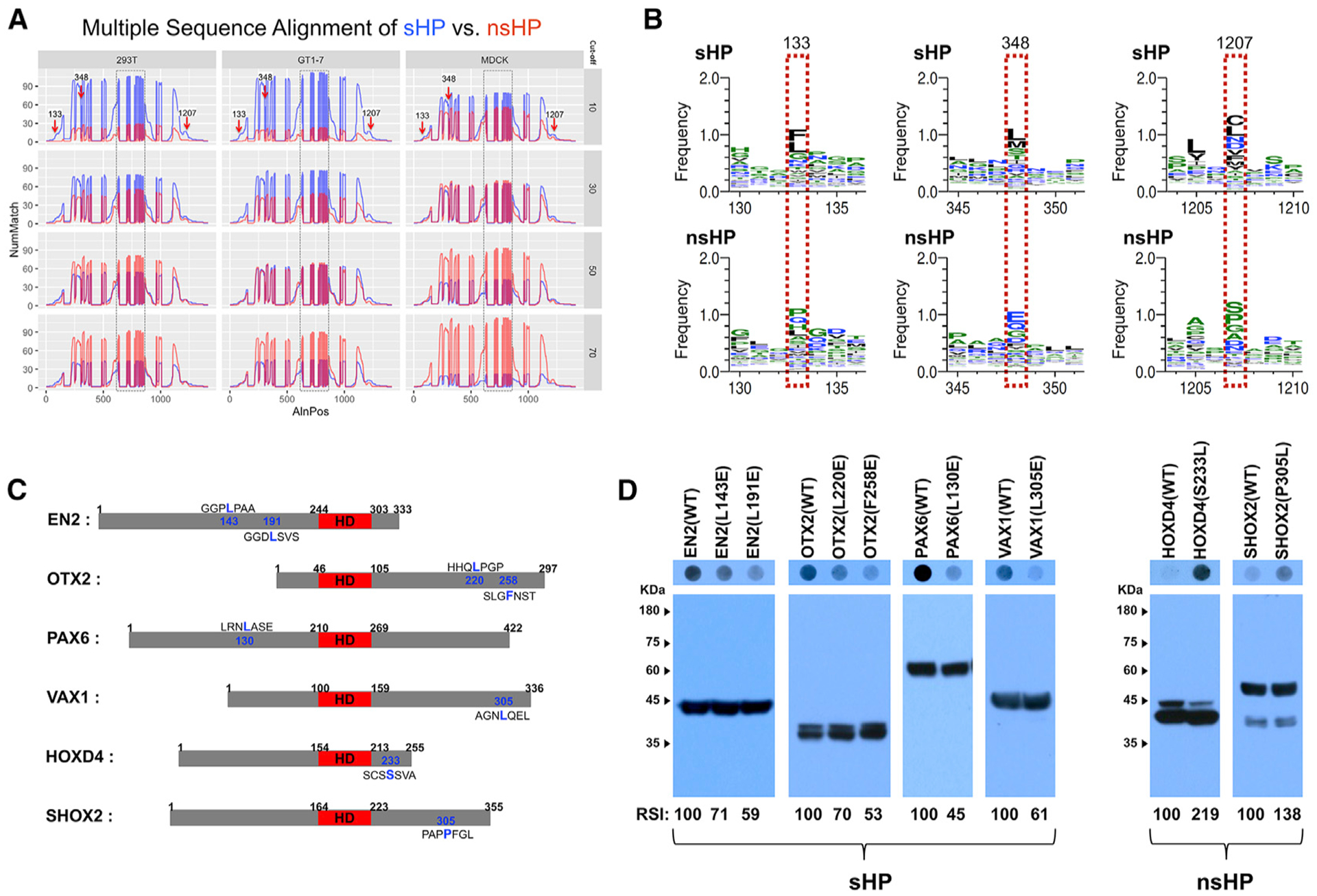
(A) Multiple sequence alignment, which is described in STAR Methods, identified shared motifs in sHPs (arrows). y axis, number of matches (NumMatch); x axis, aligned positions (AlnPos). Boxed areas are HDs, which are aligned from 626 to 849 in the plots and include gaps of unshared amino acid sequences as well as consensus motifs.
(B) Amino acid sequences in the positions pointed by arrows in (A) are different between sHP (top) and nsHP (bottom). Amino acids in each position are displayed in the order of abundance (top to bottom).
(C) Diagrams that show the locations of the amino acids, which are predicted to be shared among sHPs and nsHPs, respectively. The HDs are colored in red.
(D) Secretion abilities of those mutated proteins were determined by DB with anti-V5 antibody (top), and relative levels of HPs in the transfected cells were examined by WB with anti-V5 antibody (bottom). The scores below the WB images are average RSI values comparing with the secretion indexes of WT HPs (n = 3).
