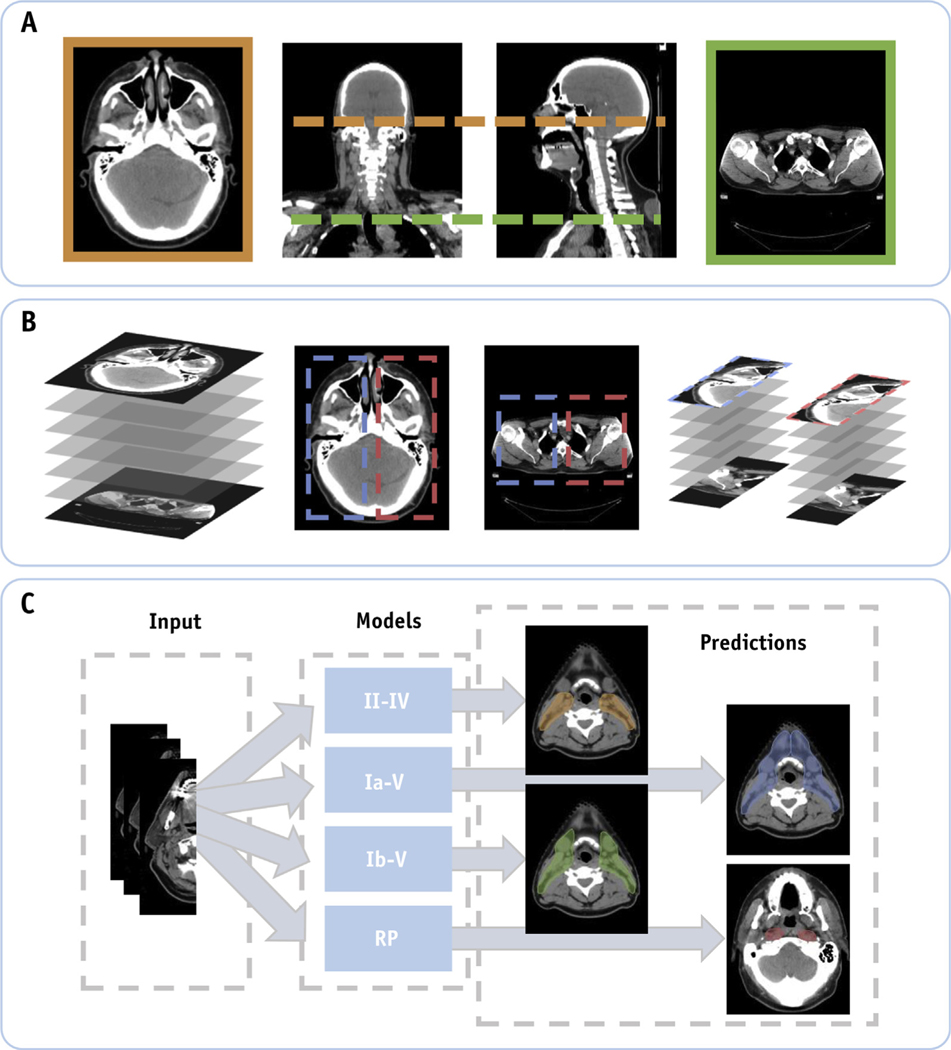
Fig. 1.
(A) Computed tomography scans of patients with head and neck cancer are normalized in the craniocaudal extent by automatically cropping out slices below and above predefined anatomic markers. (B) Identification of the left and right neck lymph node regions using computer vision techniques. Here the training data were doubled by performing a horizontal flip of the resulting input data. (C) Our deep learning model is trained using the unilateral input data to automatically segment individual lymph node target volumes.