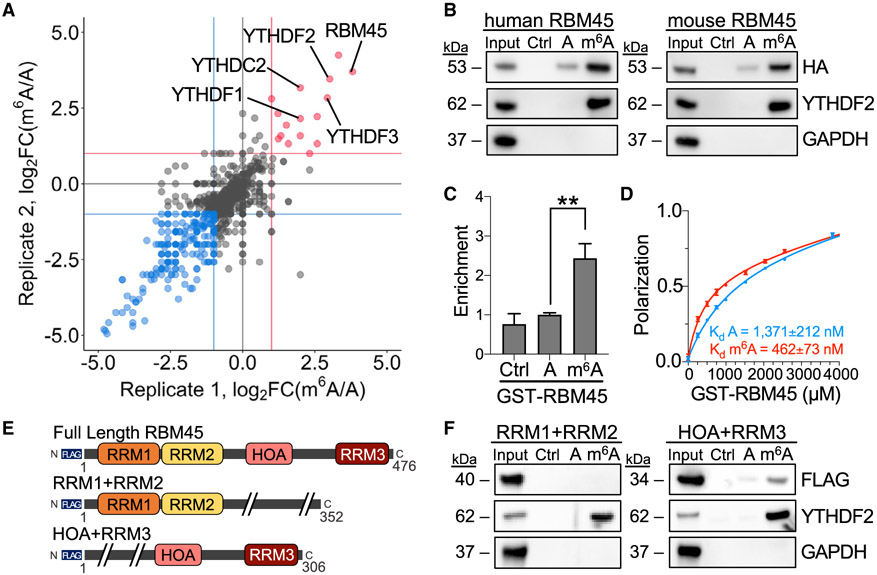
Figure 1. RBM45 binds to m6A-modified RNA.
(A) Scatterplot with proteins recovered from RNA pulldown LC-MS/MS experiments using A or m6A RNA baits and lysates from mHiPPoE-2 cells, with biological replicates plotted on each axis. RBM45 and known m6A reader proteins YTHDF1, YTHDF2, YTHDF3, and YTHDC2 are labeled. Red, proteins enriched in m6A RNA pulldowns; blue, proteins enriched in A RNA pulldown.
(B) Western blot following RNA pulldowns using lysates from HEK293T cells transfected with human or mouse HA-RBM45 shows preferential binding to m6A-modified RNA. YTHDF2 and GAPDH probed as positive and negative controls, respectively. Ctrl (no RNA), A, and m6A RNA pulldowns are indicated. Results represent 3 biological replicates.
(C) Quantification of RBM45 enrichment by Coomassie stain from RNA pulldown assays using A or m6A bait RNA and purified GST-RBM45. RBM45 enrichment is normalized to A RNA pulldown levels. Mean ± SEM plotted from 4 biological replicates. Significance calculated using a Welch’s t test; **p = 3.1 × 10−3.
(D) Fluorescence polarization assays using GST-RBM45 and A or m6A FAM-labeled RNA shows preferential binding to m6A RNA (Kd m6A = 462 ± 73 nM; Kd A = 1,371 ± 212 nM). Mean ± SD plotted for 3 biological replicates.
(E) Schematic of RBM45 variants used for RNA pulldown assays. Size indicated in amino acids.
(F) RNA pulldown results using A and m6A RNA with lysates from HEK293T cells transfected with the indicated FLAG-tagged RBM45 constructs. YTHDF2 and GAPDH are shown as positive and negative controls, respectively. Data represent 5 biological replicates.
See also Figure S1.