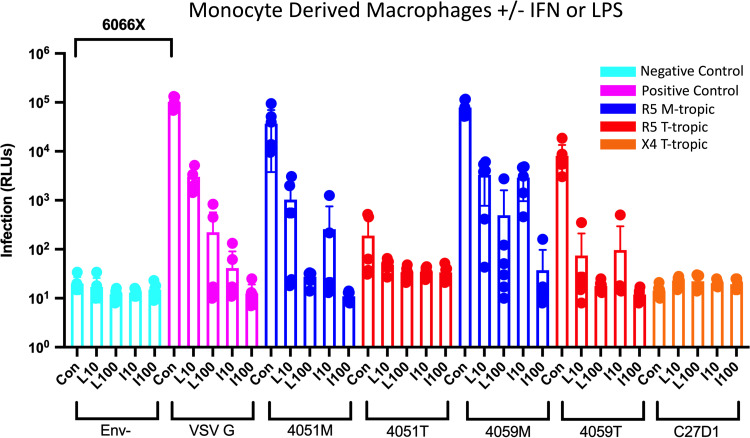
FIG 2.
Macrophage-tropic HIV-1 Env proteins confer an entry advantage over R5 T-tropic Env proteins, and LPS and IFN restrict infection in monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs). MDMs were treated with 10 ng/mL (L10) or 100 ng/mL (L100) lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or interferon alpha (IFN-α) for 24 h and then infected with HIV-1 luciferase reporter viruses pseudotyped with patient-derived R5 macrophage-tropic (blue), R5 T cell-tropic (red), or X4 T cell-tropic (orange) envelope proteins. Untreated control groups are labeled “Con” within each Env group. Negative-control viruses (cyan) lacked an envelope protein, whereas the positive-control viruses (pink) were pseudotyped with vesicular stomatitis virus G protein, which is capable of infecting a wide range of mammalian cells. The average magnitude difference between the positive and negative control was 6,066×. Infection was measured in relative light units (RLUs) via luminometer. N = 6 technical replicates.