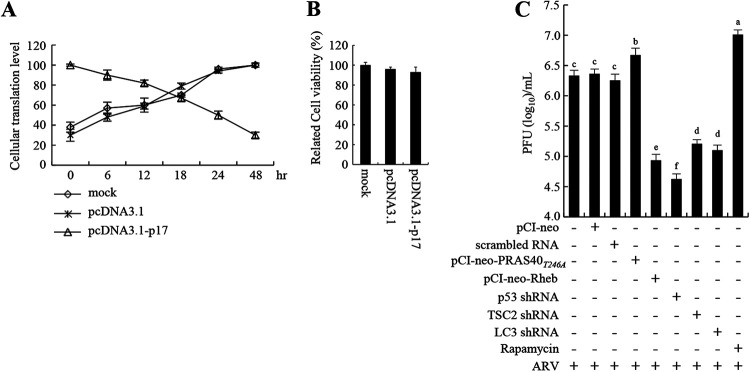
FIG 8.
ARV p17 induces translation shutoff and autophagy, benefiting virus replication. (A) Relative translation levels of cellular proteins at the indicated time points in different treatments in DF-1 cells were assayed using pulse-chase labeling. Cellular protein band intensity was assessed in relation to actin to quantify p17-regulated cellular translation shutoff. Data are means of triplicate results. (B) Cell viability in pcDN3.1 vector- or pcDN3.1-p17-transfected DF-1 cells was assessed by MTT assay. (C) The influence of the p53/Akt/mTOR pathway on ARV replication was analyzed by measuring the virus titers of different treatment groups. Vero cells were transfected with shRNAs or overexpressed PRAS40, PRAS40T24A, and Rheb for 6 h, followed by infection with ARV at an MOI of 10 for 24 h. Aside from these treatments, cells were also pretreated with rapamycin (5 μM) for 2 h, followed by infection with ARV at an MOI of 10 for 24 h. The treated- and untreated-cell lysates were collected to determine virus titers 24 h postinfection.