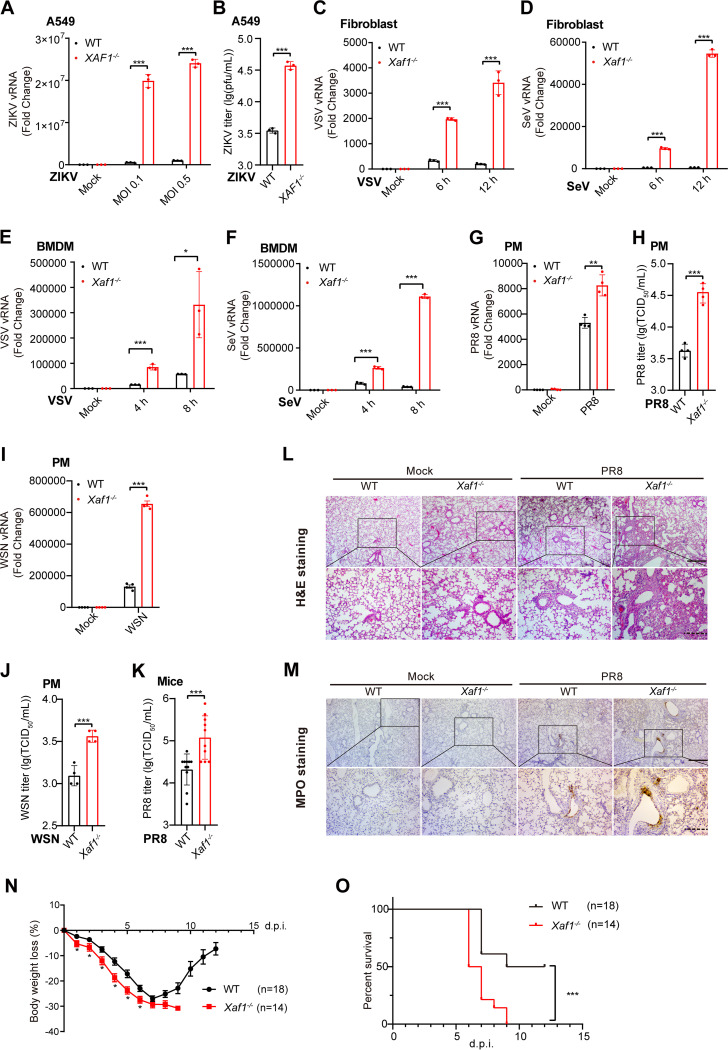
FIG 4.
Knockout of XAF1 facilitates RNA virus infection in vitro and in vivo. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of viral RNA in the WT and XAF1−/− A549 cell clones infected with ZIKV for 24 h. (B) Supernatants of (A) were measured for ZIKV plaque assays. (C and D) qRT-PCR analysis of viral RNA in the WT and Xaf1−/− fibroblast infected with VSV (MOI 1) (C) or SeV (MOI 0.1) (D) for the indicated time points. (E and F) qRT-PCR analysis of viral RNA in the WT and Xaf1−/− BMDMs infected with VSV (MOI 1) (E) or SeV (MOI 0.1) (F) for the indicated time points. (G) qRT-PCR analysis of viral RNA in the WT and Xaf1−/− PMs infected with PR8 (MOI 0.1) for 8 h. (H) TCID50 assays of supernatants from the WT and Xaf1−/− PMs infected with PR8 (MOI 0.1) for 12 h. (I) qRT-PCR analysis of viral RNA in the WT and Xaf1−/− PMs infected with WSN (MOI 0.1) for 8 h. (J) TCID50 assays of supernatants from the WT and Xaf1−/− PMs infected with WSN (MOI 0.1) for 12 h. (K) TCID50 assays of the lung homogenates from the WT (n = 11) and Xaf1−/− (n = 10) mice infected with PR8 (100 PFU) intranasally for 5 d. (L and M) Histological examination of the lung sections from the WT and Xaf1−/− mice infected with PR8 (100 PFU) intranasally for 5 d was performed by H&E staining (L), and neutrophil infiltrations of the lung sections from the indicated mice were measured by MPO staining (M); scale bar, “—” represents 400 μm; “‐‐‐” represents 200 μm; data are representative results of three independent experiments. (N and O) Survival assays of the WT and Xaf1−/− mice infected with PR8 (100 PFU) intranasally (WT group: n = 18; Xaf1−/− group: n = 14). Bodyweight loss curves (N) and Kaplan-Meier survival curves (O) were generated and analyzed from three independent experiments; *, P < 0.05 and ***, P < 0.001 indicate significant difference. Data of (A–K) from three independent experiments are presented as mean ± SD; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; and ***, P < 0.001 indicate significant difference by unpaired Student's t test.