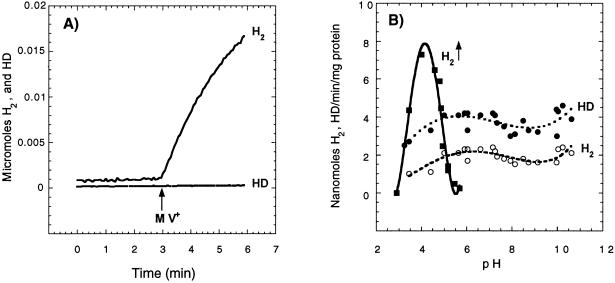
FIG. 6.
HupUV hydrogenase activities in the soluble cytosolic fraction of JP91(pAC206) cells as a function of pH. JP91(pAC206) cells grown photoheterotrophically in MN medium were broken by passage through a French pressure cell. The soluble cytoplasmic fraction obtained by centrifugation at 100,000 × g for 70 min was used to determine HupUV hydrogenase activities. (A) H2 production linked to MV oxidation at pH 4.0. The phosphate-citrate buffer (1.25 ml, final concentration of 100 mM) in the reaction chamber was first sparged with argon to remove O2, and then the reaction vessel was closed, and 0.25 ml of soluble cytosolic fraction (0.9 mg of protein) was added. Two minutes later, MV+ (50 μl, final concentration of 120 mM) was injected into the reaction vessel. (B) pH dependence of MV+-mediated H2 production and H2 and HD formation in exchange with D2. Initial rates determined for the first minute of H2 (○) and HD (●) production (in 1.5 ml, 0.8 mg of protein) are plotted versus pH. To measure the H-D exchange, the reaction vessel was sparged first with D2. H2 (■) was formed by proton reduction with MV+. The buffers used (final concentration of 100 mM) were phosphate-citrate (pH 2.9 to 7.0), phosphate-Tris (pH 6.6 to 8.5), phosphate-glycine-NaOH (pH 7.5 to 10), and glycine-NaOH (pH 9.0 to 12.8).