Figure 5. The S1P signaling pathway during disease (CAD).
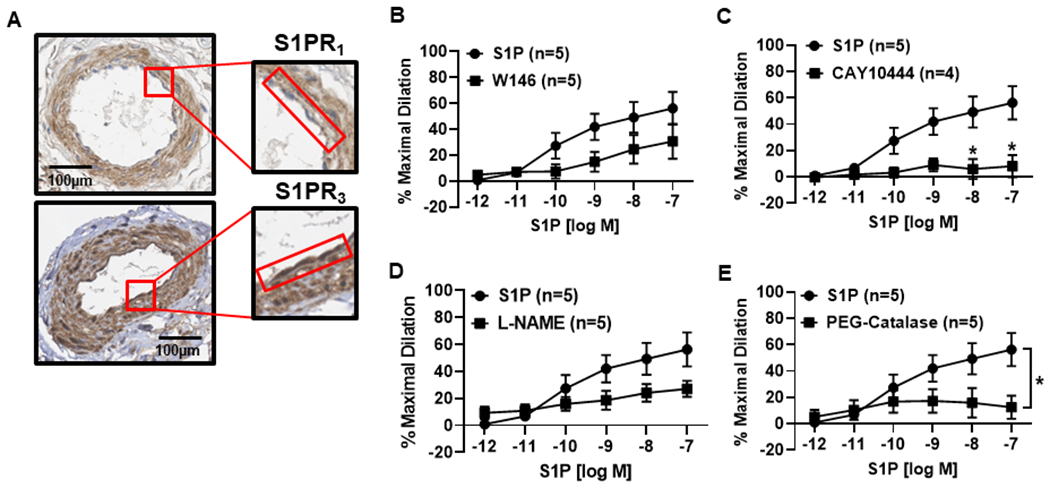
A) Representative immunohistochemistry (IHC) images showing staining (representative images of n=5) of S1P receptors 1 and 3 in the microvascular endothelium from patients with CAD. The endothelium is highlighted by the red box. B) S1P induced a dose-dependent dilation (10−12 to 10−7) was not significantly reduced in the presence of the S1PR1 inhibitor W146 (10μM, n=5) in arterioles collected from patients diagnosed with CAD. (C) Dilation to S1P was significantly impaired during exposure to the S1PR3 inhibitor CAY10444 (10μM, n=5) compared to S1P alone (n=5). D) In vessels from patients with CAD, dilation was not significantly impaired with the addition of L-NAME (100μM, n=5), but was significantly reduced in the presence of PEG-Catalase (500U, n=5) (E). Data are expressed as mean % maximal dilation±SEM., *p<0.05 compared to S1P treatment alone.
