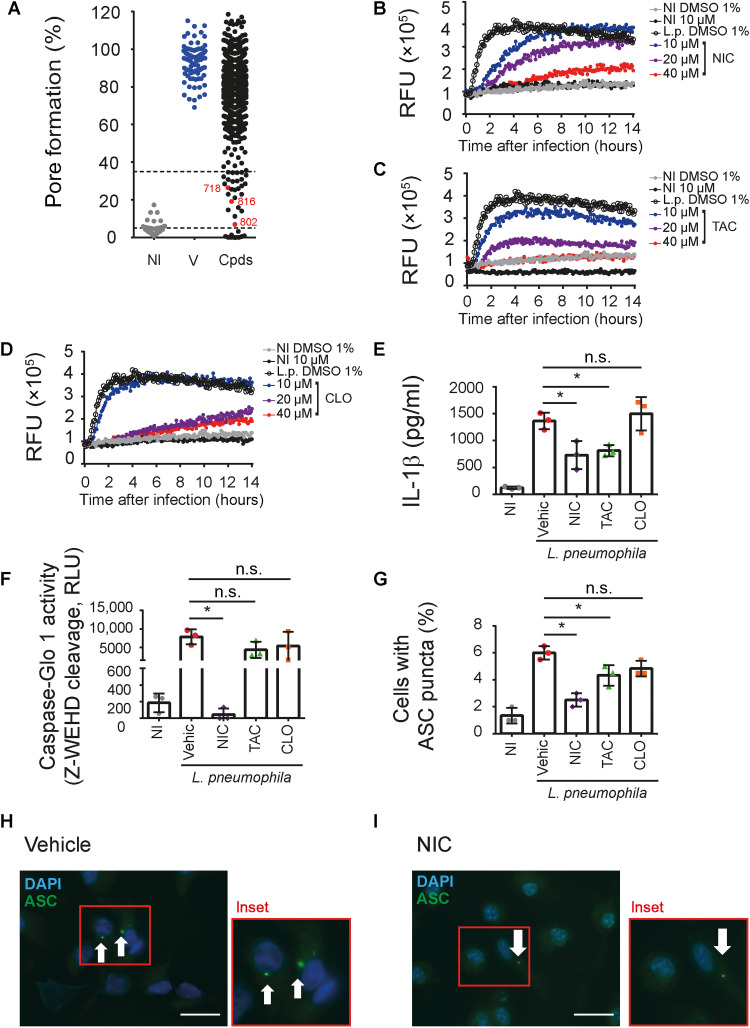
Fig. 1. A high-throughput screening identifies anti-inflammasome drugs.
(A) BMDMs were primed with lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 500 ng/ml) for 3 hours, treated with different library compound at 10 μM, and infected with L. pneumophila at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 10. Pore formation was quantified by PI uptake after 3 hours infection. Triton X-100 was used to determine 100% PI uptake. Each dot represents the activity of one compound. NI, noninfected controls; V, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) controls; Cpds, tested compounds. The drugs 718 (NIC), 802 (TAC), and 816 (CLO) are highlighted in red. The dotted lines indicate the 65 to 95% range of pore formation inhibition used for the initial selection. (B to D) Kinetics of pore formation in BMDMs infected or NI with L. pneumophila for 14 hours. Pore formation was estimated by PI internalization [relative fluorescence units (RFU)]. (E and F) BMDMs were primed with LPS for 3 hours; treated with 10 μM NIC, TAC, or CLO or 1% DMSO (Vehic) for 1 hour and infected with L. pneumophila (MOI of 10). Cell supernatants (SNs) were assayed for IL-1β (E), caspase-1 activity (F), and percentage of cell containing ASC puncta (G). Representative images of ASC puncta (green) in L. pneumophila–infected BMDMs treated with vehicle (H) or NIC (I) are shown. Scale bars, 30 μm. *P < 0.05. n.s., nonsignificant as determined by Student’s t test. Data are presented from one representative experiment of three experiments performed with similar results.