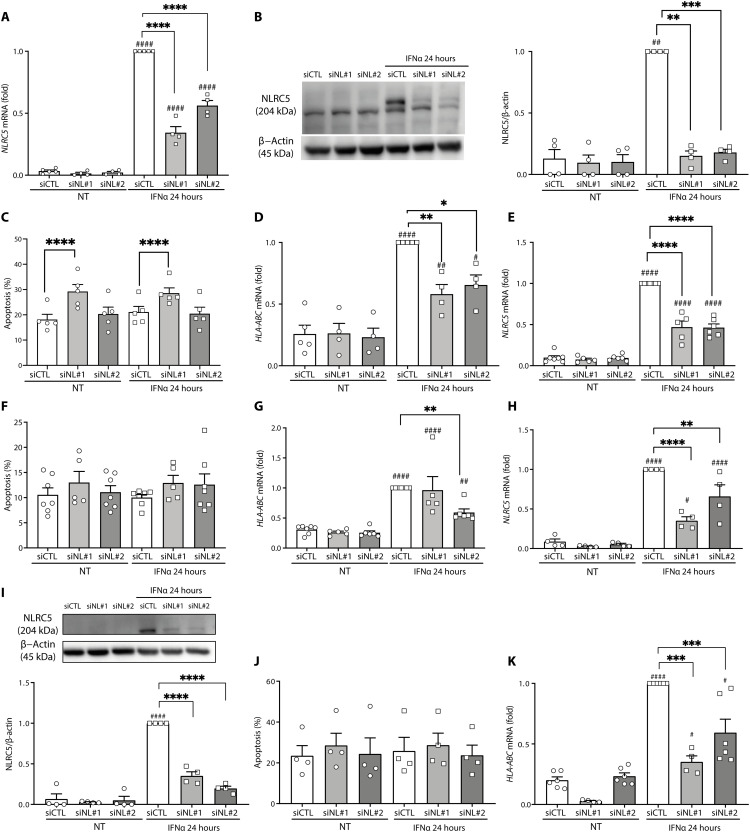
Fig. 3. NLRC5 KD decreases IFNα-induced HLA-ABC expression in human pancreatic β cells.
(A to D) EndoC-βH1 cells, (E to G) dispersed human islets, and (H to K) iPSC-derived β-like cells were transfected with siRNA control (siCTL, white bars) or with two different siRNAs targeting NLRC5 (siNL#1 and siNL#2, gray bars). Cells were left untreated or treated with IFNα (2000 U/ml) for 24 hours. Expression of NLRC5 mRNA was measured by RT-PCR (A, E, and H), and NLRC5 protein was determined by Western blotting (B and I). The percentage of dead cells was counted by Hoechst and propidium iodine staining (C, F, and J). NLRC5 depletion decreased IFNα-induced expression of HLA-ABC (D, G, and K). The mRNA expression was analyzed by RT-PCR and normalized by the geometric mean of GAPDH and β-actin and then by siCTL treated with IFNα considered as 1. NLRC5 protein was quantified by densitometry and normalized by the housekeeping protein β-actin and then by the highest value of each experiment considered as 1. Results are means ± SEM of four to seven independent experiments. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, and ####P < 0.0001 versus untreated and transfected with the same siRNA; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001, as indicated by bars (ANOVA followed by Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons).