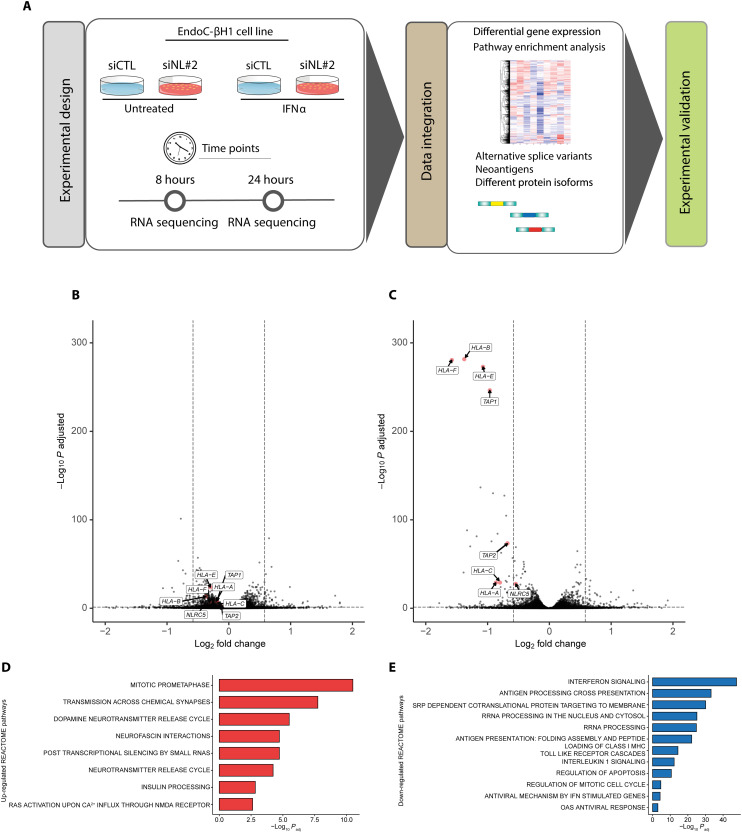
Fig. 4. RNA-seq of EndoC-βH1 cells after IFNα exposure preceded or not by NLRC5 depletion.
(A) Methodologic approach for the RNA-seq experiments. EndoC-βH1 were transfected with siRNA control (siCTL) or with an siRNA targeting NLRC5 (siNL#2). The cells were left untreated or treated with IFNα (2000 U/ml) for 8 or 24 hours. The RNA-seq was performed for all the conditions (n = 6), and DGE and alternative splicing analysis were performed as described in Materials and Methods. (B and C) Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes in EndoC-βH1 after 8 hours (B) and 24 hours (C) of exposure to IFNα with KD of NLRC5. Quantification of the RNA-seq data was performed using Salmon with GENCODE v36 as the genome reference. DGE was performed using DESeq2. (D and E) GSEA analysis. Results from the DGE analysis were input in fGSEA. Selected enriched pathways (D) showed a functional recovery of EndoC-βH1 cells, while selected depleted pathways (E) indicated that the previously IFNα-induced signature was reversed following KD of NLRC5. The output of the fGSEA analysis is provided in data file S3.