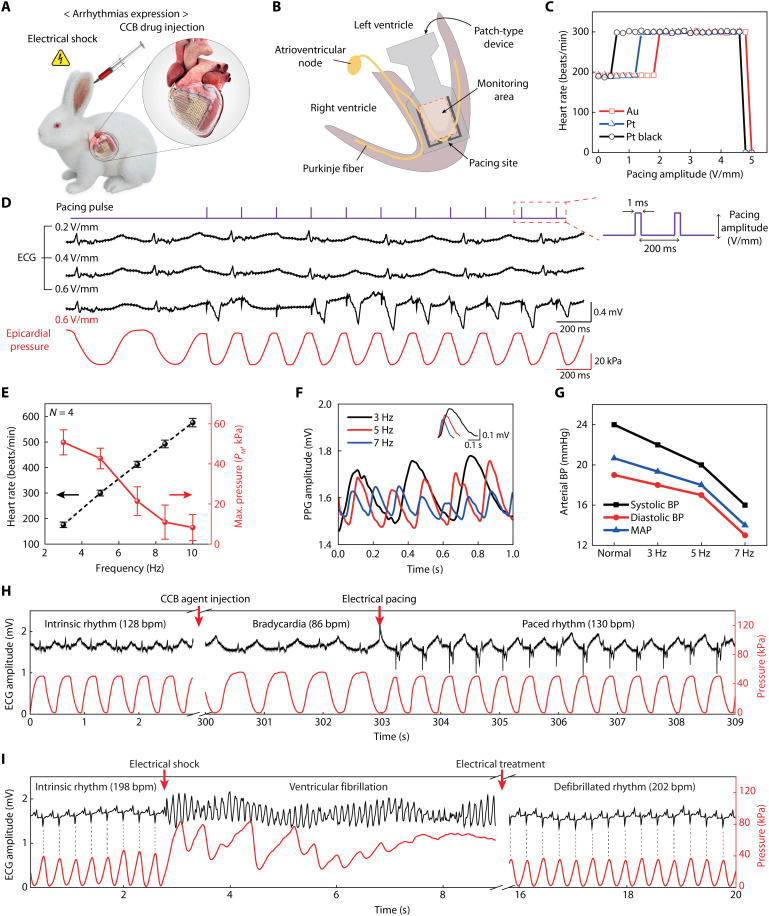
Fig. 6. In situ diagnosis and treatment of cardiac arrhythmia.
(A) Schematic illustration on a live rabbit model for the arrhythmia expression by CCB drug injection and electrical shock. (B) Schematic illustration on the cross-section of a heart, indicating respective sites for the monitoring of cardiac beating motion and electrical pacing. (C) Electrical pacing characterization for successful heart rhythm modulation using three different pacing electrodes of Au, Pt, and Pt black (pacing condition: 5 Hz in frequency, 1 ms in pulse width). (D) Comparison between the surface ECG and epicardial pressure detection traces, according to pacing amplitude using the Pt black electrodes. (E) Synchronized heart rate and PM measured by the device platform with respect to different pacing frequencies. (F) Real-time measurements of the photoplethysmogram at different pacing frequencies. The inset plots the magnified peaks of the photoplethysmogram, which compares the PPG amplitudes at different heart rates (3, 5, and 7 Hz). (G) Measurement of femoral arterial BP of the systole and diastole phases at different pacing frequencies. The mean arterial pressure values were calculated from the systole and diastole BP at respective pacing frequencies. (H) In situ diagnosis and simultaneous treatment of bradycardia using the device platform. Restoration to intrinsic heart rhythm after electric pacing (0.6 V/mm, 2.2 Hz, 1 ms) using the device platform was performed while continuously monitoring epicardial pressures (red line) and surface ECG (black line). (I) In situ diagnosis and simultaneous treatment of the expressed LV fibrillation using the device platform (red line), with comparison to the surface ECG trace (black line). For ventricular defibrillation, restoration to intrinsic heart rhythm by electrical treatment (7 V/mm, 1 s) was performed using this device platform. Dashed lines indicate the synchronized heartbeats between the ECG and pressure traces.