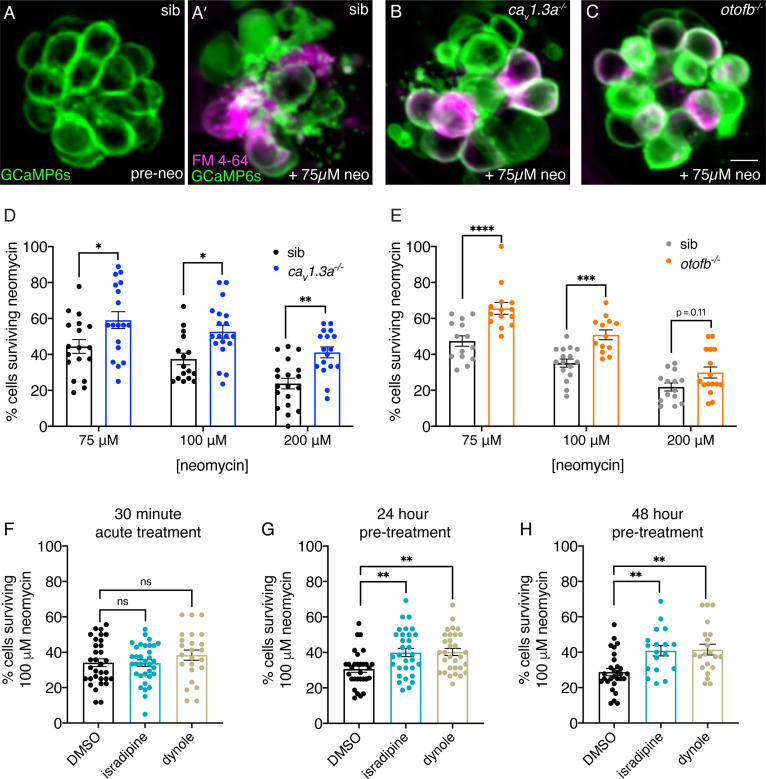
Figure 2. Chronic loss of neurotransmission protects hair cells from the ototoxin neomycin.
(A-A’) Hair cells in siblings before (A) and after a 30-min treatment with 75 µM neomycin (A’). GCaMP6s outlines hair cells. The presence of FM 4–64 in hair cells reveals surviving cells (A’). (B-C’) After a 30-min treatment with 75 µM neomycin GCaMP6s and FM 4–64 more surviving hair cells are found in cav1.3a-/- (B), and otofb-/- (C) mutants. (D–E) A higher percentage of CaV1.3- and Otof-deficient hair cells survive a 30 min treatment with three different neomycin concentrations (75, 100, and 200 µM) compared to sibling controls. For quantification in D-E, neuromasts were examined at 5 or 6 dpf immediately after washout of neomycin solution and application of FM 4–64. (F) Percentage of hair cells per neuromast surviving is not altered when hair cells in wildtype larvae are co-incubated with 0.1% DMSO (control), 10 µM isradipine, or 2.5 µM Dynole 34–2 during the 30-min 100 µM neomycin treatment. (G–H) When wildtype hair cells are incubated with 10 µM isradipine or 2.5 µM Dynole 34–2 for 24 hr (G, 4 to 5 dpf) or for 48 hr (H, 3 to 5 dpf) prior to neomycin treatment significantly more hair cells survive compared to DMSO controls. Each point in the dot plots in D-H represents one neuromast. A minimum of five animals were examined per treatment group. Error bars: SEM. For comparisons, a two-way ANOVA with a Sidak’s correction for multiple comparisons was used in D-E. A one-way AVOVA with a Dunnett’s correction for multiple comparisons was used in F, G and H. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001. Scale bar = 5 µm.