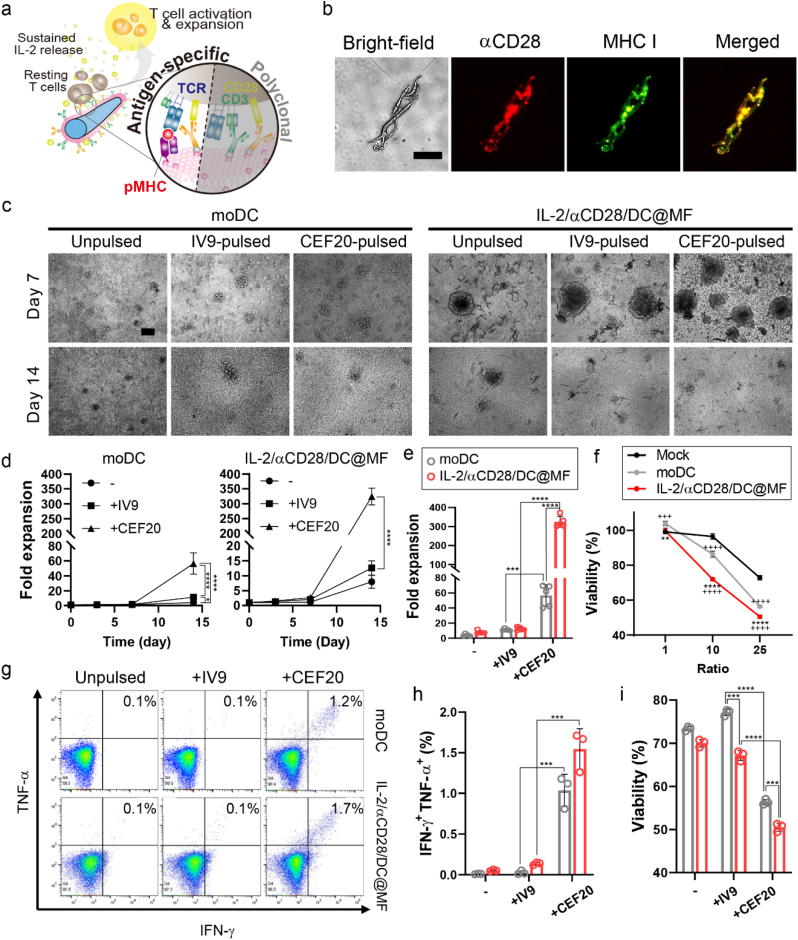
Fig. 5.
Antigen-specific expansion of primary human T cells. (a) Schematic of antigen-specific T cell expansion stimulated by IL-2/αCD28/DC@MF. (b) Fluorescence microscopy images of IL-2/αCD28/DC@MF stained with an anti-mouse IgG antibody (red) and an anti-human HLA-A2 antibody (green) (scale bar, 50 μm) for detecting αCD28 and MHC I, respectively. (c) Bright-field microscopy images of CMV-specific T cells cultured with autologous monocyte-derived DC (moDC) or IL-2/αCD28/DC@MF (scale bar, 100 μm). Prior to culture, moDC were pulsed with IV9 or CEF20 (HIV or CMV antigen peptides, respectively) and IL-2/αCD28/DC@MF was loaded with those antigen peptides. (d) T cell expansion profiles of the moDC and IL-2/αCD28/DC@MF groups. -, unpulsed; +IV9, pulsed/loaded with HIV antigen peptides; +CEF20, pulsed/loaded with CMV antigen peptides. (e) Fold expansion at day 14 of CMV-specific T cell culture. (f–i) In vitro T cell functional studies. CMV-specific T cells expanded for 14 days were co-cultured with T2 cells pulsed with CEF20. (f) Viability of T2 target cells at varying T2-to-T cell ratios. (g, h) Flow cytometric analysis showing IFN-γ and TNF-α cytokine production of T cells co-cultured with T2 cells at a ratio of 25. (i) T2 cell viability at a ratio of 25 after 4 h of co-culture. Data in (d–i) represent mean ± s.d of n = 3 and are representative of at least two independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001; two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc tests.