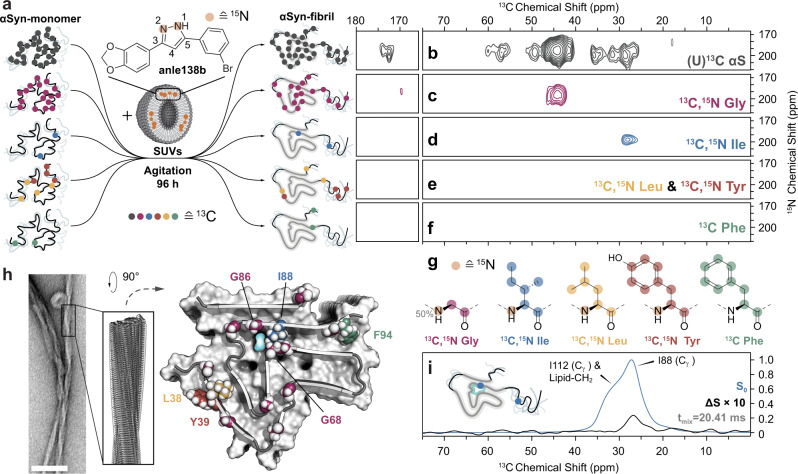
Fig. 1. Identification of anle138b binding inside α-synuclein fibrils by DNP-enhanced MAS NMR.
a Isotope labeling strategy used for the preparation of fibril samples for studies by DNP-enhanced MAS NMR. 13C-labeling of amino acids indicated by colored circles: unifom- (gray), Gly- (magenta), Ile- (blue), Leu- (yellow), Tyr- (red), and Phe-labeling (green). 15N-labeling on anle138b indicated by orange circles. b–f Slices of 2D NHHC spectra of α-synuclein fibrils prepared from protein with b uniform 13C-labeling and c–f amino-acid-specific isotope labeling on c Gly, d Ile, e Leu and Tyr, and f Phe in the presence of 1,2-15N-anle138b. The spectral region shown contains only cross-peaks between pyrazole NH of anle138b (195 ppm) and protein carbon atoms. Proton–proton mixing was 200 μs. g Chemical structures of amino acids used for specific isotope labeling with 13C- labeled nuclei indicated by colored circles (same as in a) and 15N-labeling indicated by orange circles. h Negative stain EM micrograph of fibrils grown in the presence of lipids (scale bar 100 nm) alongside cryo-EM structure of α-synuclein protofilament L220 with color coding of specific isotope-labeled residues. i Frequency selective REDOR spectrum (carrier frequency at 26 ppm, Supplementary Table 2) of Ile-labeled α-synuclein fibrils in the presence of 1,2-15N-anle138b. The difference spectrum (ΔS) is scaled up 10-fold with respect to the reference spectrum (S0) for clarity. Fibrils were prepared at a lipid to protein to anle138b molar ratio of 10:1:0.5. All spectra were recorded at 600 MHz at 100 K (see Supplementary Table 1) in the presence of TEMTriPol-1.