Figure 1.
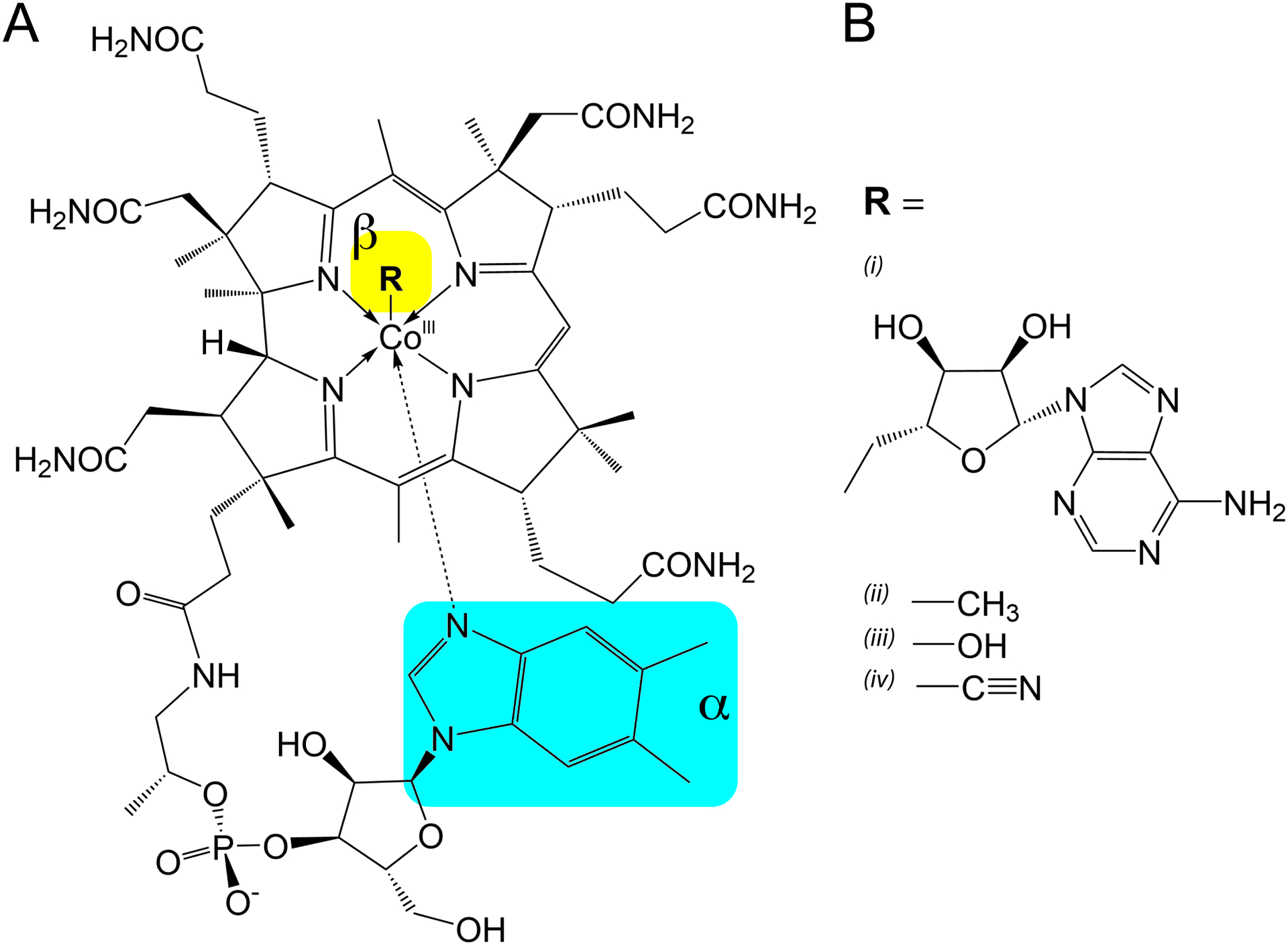
Structure of cobalamin with variable beta-axial moieties (R) which determine its form. (A) The common cobalamin corrin ring shared between all forms shown here, with the 5,6-dimethylbenzimidzole coordinated to the alpha-axial face. Arrows are used to depict coordinate bonds with the cobalt (III) ion as opposed to covalent bonding. The alpha- and beta-axial positions are highlighted in cyan and yellow, respectively. (B) Variable functional moieties that can be present in the beta-axial position of the corrin ring. (i) 5’-deoxyadenosylcobalamin (ii) methylcobalamin (iii) hydroxocobalamin (iv) cyanocobalamin.
