Figure 6. Vaccine expanded L54 IGHV1-69 memory B cells are cleared limiting boosting to the HA stalk.
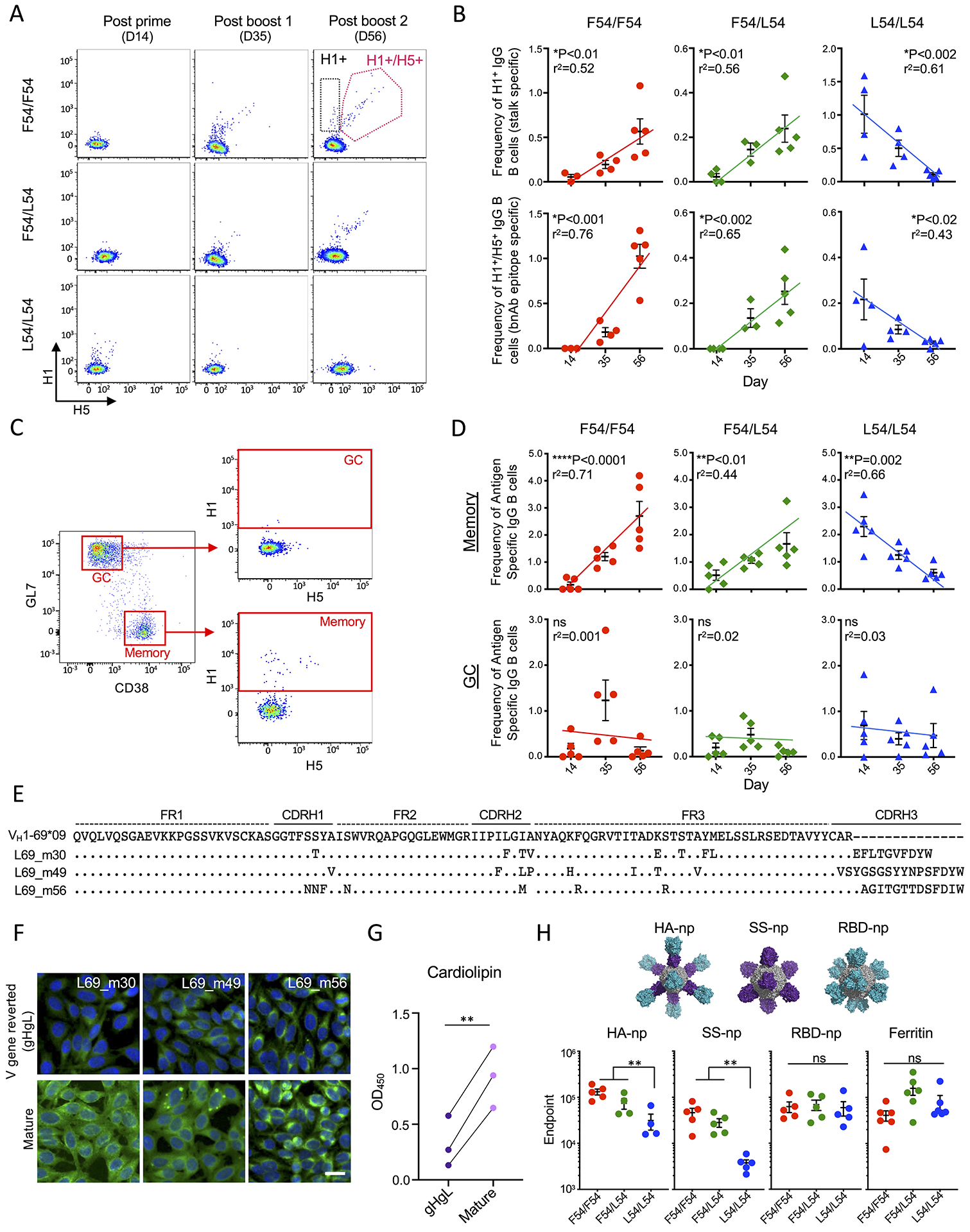
(A) Antigen specific IgG B cells were measured by flow cytometry during SS-np immunization. Reactivity to H1 trimer (black box) and reactivity to H1 + H5 trimers (pink box) (B) Quantification of H1+ and H1+/H5+ reactive IgG B cells following SS-np immunization at D14, D35, D56 (mean and SEM, n=3–5 mice per genotype, linear regression). (C) Gating strategy for distinguishing antigen specific B cells (H1+ and H1+/H5+ reactive) in the GC and memory compartments. Gated on CD4−/F4.80−/Gr-1−/CD19+/IgD− B cells (Tan et al., 2019). (D) Frequency of stalk reactive (H1+ and H1+/H5+ reactive) IgG B cells in GC and memory compartments at D14, D35, and D56 (mean and SEM, n=5 mice per genotype, linear regression). (E) Individual L54 stalk IgG (H1+/H5+) B cells expanded during the SS-np immunization regimen. (F) Hep2 reactivity of antibodies from (E) and their V gene-reverted (VHVL) sequences. (G) Cardiolipin reactivity of antibodies from (E) and their V gene-reverted (VHVL) sequences (**P<0.006, Paired T-test). (H) Endpoint titer of antigen specific IgG following sequential immunization with full length HA nanoparticle (HA-np); stalk only HA nanoparticle (SS-np), receptor binding domain nanoparticle (RBD-np). All HA sequences are derived from H1N1 NC99 and display the stalk domain (purple) and/or head domain (teal), and ferritin scaffold (grey). Endpoint titers following sequential immunization are shown at post boost 2 (D56) (mean and SEM, n=5 mice per genotype, **P<0.01, ANOVA with Tukey’s test). NC99 HA trimer baits are used for endpoints to HA-np, SS-np, and RBD-np and ferritin bait was used for SS-np immune sera.
