Figure 1 |. Risk for ASD is attributable to multiple genetic factors including DNMs, rare inherited variants and polygenic risk.
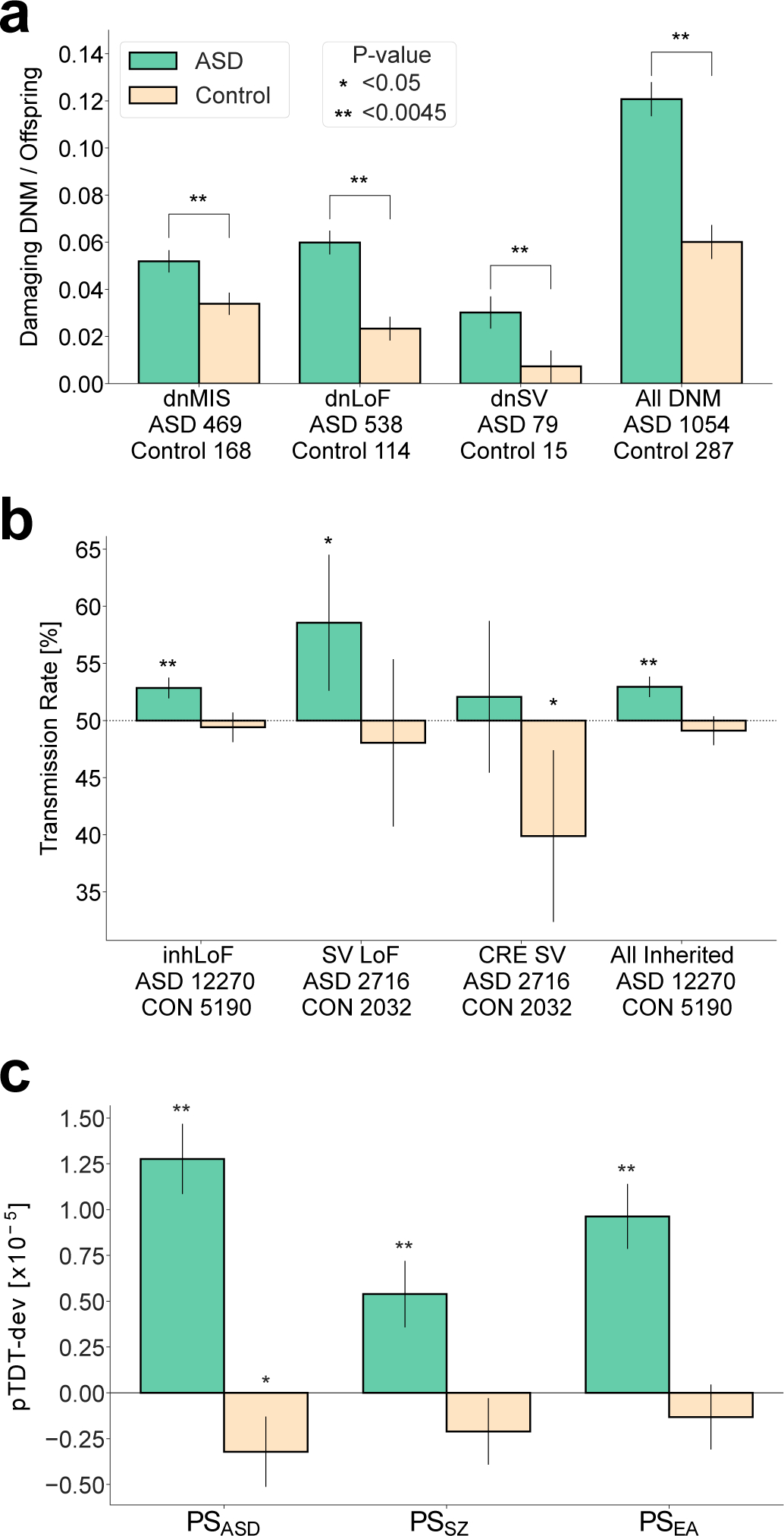
Multiple genetic factors that have been previously associated with ASD were confirmed in our combined sample. “**” denotes associations that were significant after correction for 11 tests (P < 0.0045). Error bars represent the 95% confidence intervals. a, Damaging DNMs in genes that are functionally constrained (LOEUF < 0.37 and MPC ≥ 2), including missense variants (dnMIS), and protein-truncating SNVs and indels (dnLoF) and SVs (dnSV), occur at higher frequencies in cases than in sibling controls. P-values were based on two-sided t-tests. b, Protein-truncating SNVs and indels (inhLOF) and SVs (SVLoF) and non-coding SVs that disrupt cis-regulatory elements (CRE-SVs) were associated with ASD based on a TDT test. c, Polygenic TDT (pTDT) was significant for all three polygenic scores for autism (PSASD), schizophrenia (PSSZ), and educational attainment (PSEA). Rare variant associations (a,b) were tested in the full sample (n = 37,375). Polygenic pTDT association was tested in samples of European ancestry (n = 25,391). Results for a-c and full lists of rare de novo and inherited variants in constrained genes are provided in Supplementary Tables 3–10.
