Figure 5.
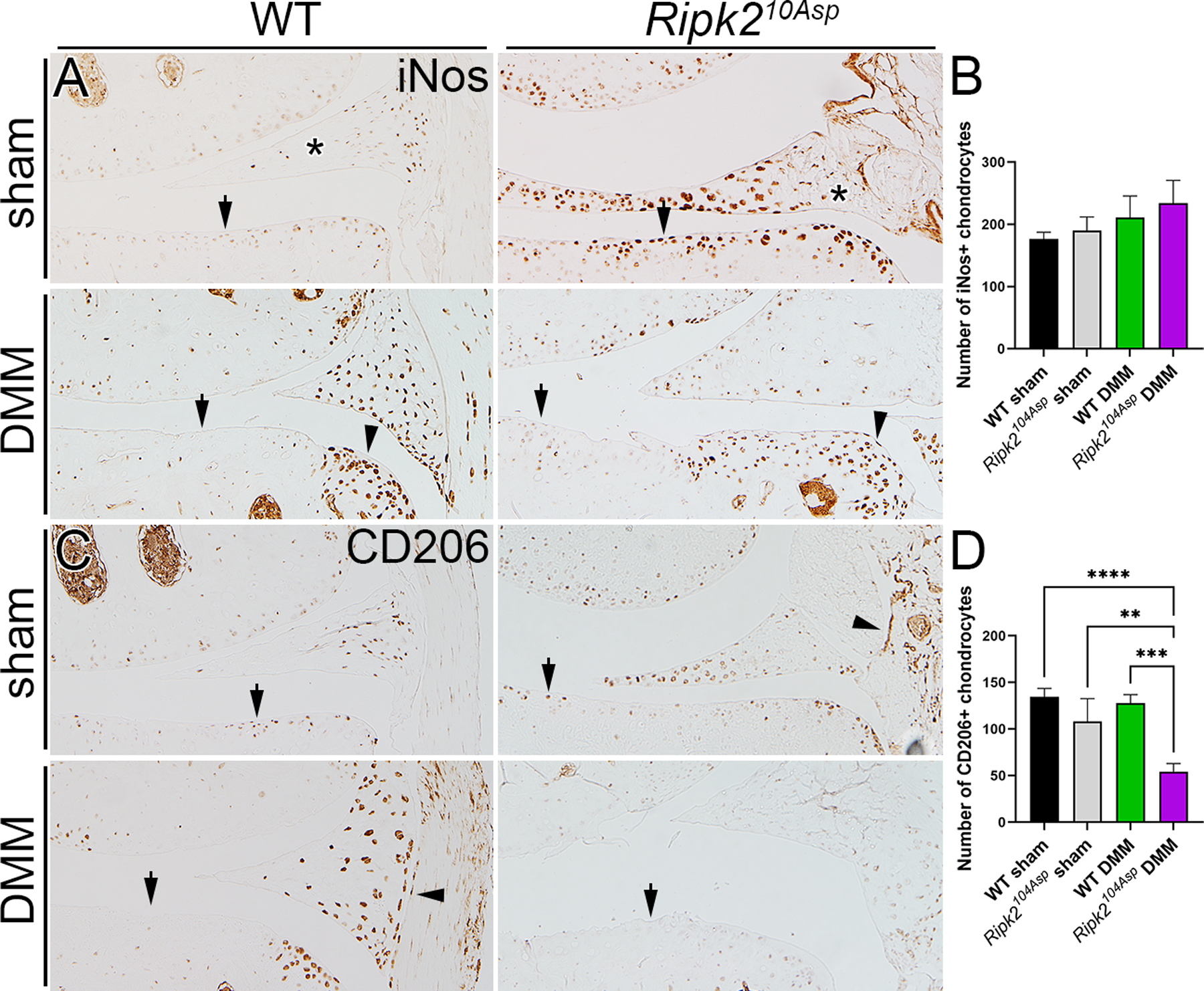
Ripk2104Asp joints have elevated expression of proinflammatory markers. (A) In WT mice, the proinflammatory marker iNos is normally expressed at low levels in the joint, and is markedly elevated following DMM surgery. In contrast, knee joints of Ripk2104Asp have chronically high levels of iNos expression, independent of injury. In A arrows indicate chondrocytes, asterisks mark the meniscus, and arrowheads indicate osteophytes in DMM-operated joints. (B) There is no difference in expression of the anti-inflammatory marker, CD206, between sham-operated surgery WT and Ripk2104Asp joints. Following DMM surgery, CD206 is prominently expressed in WT joints whereas it is almost absent in the joints of Ripk2104Asp mice. In B arrows indicate chondrocytes and arrowheads indicate synovium. All joints are 8 weeks post-surgery. C) Quantification of the number of iNos and CD206 positive chondrocytes in the medial knee joint of WT sham, Ripk2Asp104 sham, WT DMM, and Ripk2Asp104 DMM mice. n = 3 independent animals for each experimental condition. Error bars represent ±SD and statistically significant differences of P ≤ 0.01 (**), P ≤ 0.001 (***), and P ≤ 0.0001 (****) were determined by two-way ANOVA with Tukey‟s multiple comparisons test.
