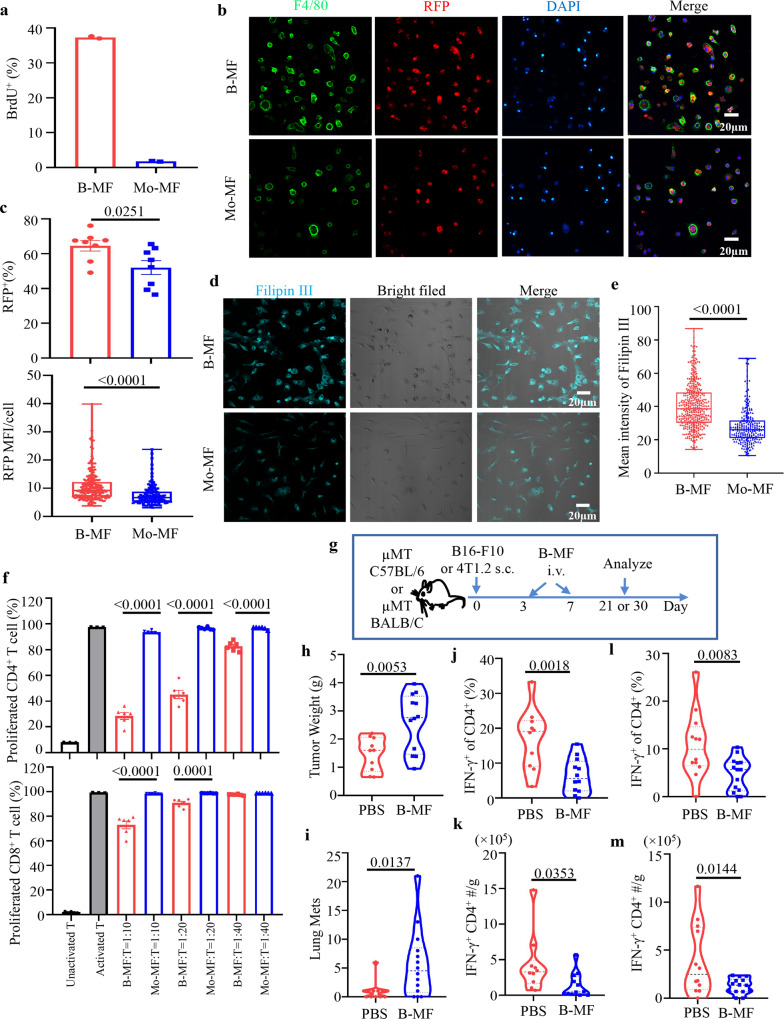
Fig. 4. B-MF and Mo-MF are functionally different.
a Unlike Mo-MF, B-MF incorporate BrdU, i.e., proliferate (BrdU+ frequency ± SEM from 2 mice per group). Compared to Mo-MF, B-MF exhibit higher ability to phagocytize apoptotic ID8-RFP cells than Mo-MF in 2 h assay (b, c) and to bind Filipin III (d, e). Panels b, d show representative fluorescent microscopy images of quantifications of RFP+ cells % ±SEM (P = 0.0251) and RFP MFI/cell (P < 0.0001) (Mean Fluorescence Intensity MFI, c) and Filipin III MFI (P < 0.0001, e) difference between B-MF and Mo-MF. Eight representative fields per sample were quantified and scale bars represent 20 μm (c, e). f Unlike Mo-MF, B-MF efficiently suppress proliferation of T cells stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 Abs for 4 days (P < 0.0001 except for CD8 + T cell 40:1 group). Y-axis is for Mean proportion ± SEM of CSFE-diluted (n = 3 for nonactivated and activated control groups, and n = 6 for the rest groups) CD4+ or CD8+T cells when incubated with B-MF or Mo-MF at 10:1, 20:1, and 40:1 ratio (X-axis). Control T cells were cultured alone with (activated) or without (nonactivated) anti-CD3/CD28 Abs. Panels b–f were independently reproduced at least three times. g–m B-MF support tumor progression. Schema of adoptive transfer experiments in μMT C57BL/6 and BALB/CJ mice with s.c. B16-F10 melanoma and 4T1.2 cancer depicted in g. In vitro-generated B-MF (3 × 105) from C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice were i.v. transferred into μMT C57BL/6 and μMT BALB/c mice, respectively, at days 3 and 7 post-tumor challenge. Shown are quantifications of tumor weight in mice with B16-F10 melanoma (n = 10 for PBS and n = 12 for B-MF, P = 0.0053, h), metastatic foci in the lungs of mice with 4T1.2 cancer (n = 12 for PBS and n = 14 for B-MF, P = 0.0137, i), and frequency and absolute numbers of IFNγ+CD4+ T cells per gram primary tumor in mice with B16-F10 melanoma (j, P = 0.0018 and k, P = 0.0353) and 4T1.2 cancer (l, P = 0.0083 and m, P = 0.0144). P-values in c, e, f, h–m was calculated using two-tailed unpaired t-test. Results were independently confirmed at least twice. Each symbol in h–m is for a single mouse.