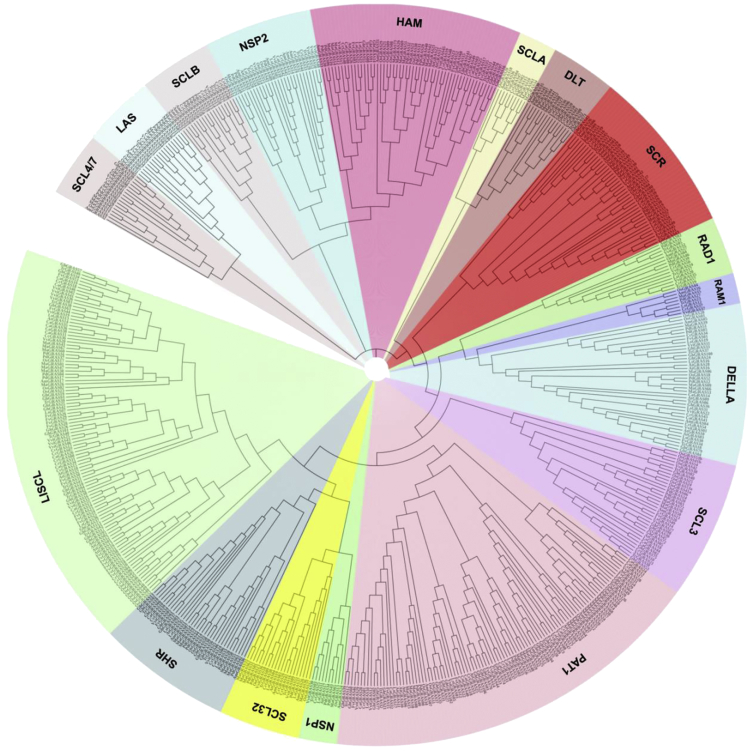
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic analysis of GRASs in plant species
Phylogenetic tree of GRAS proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana (Lee et al., 2008), Amborella trichopoda (Albert et al., 2013), Capsicum annum (Liu et al., 2018), Coffea canephora (Denoeud et al., 2014), Fragaria vesca (Chen et al., 2019a), Gossypium hirsutum (Zhang et al., 2018), Lagenaria siceraria (Sidhu et al., 2020), Musa acuminate (D’Hont et al., 2012), O. sativa (Tian et al., 2004), Phoenix dactylifera (Al-Mssallem et al., 2013), Theobroma cacao (Argout et al., 2011), and Vitis vinifera (Grimplet et al., 2016). GRAS protein sequences are aligned using MUSCLE package available in MEGA X software (Stecher et al., 2020). The phylogenetic tree was created using the neighbor-joining (NJ) method with the Poisson model, pairwise deletion, and 1,000 bootstraps values. The phylogenetic tree was visualized using the iTOL online tool (Letunic and Bork, 2021). The GRAS proteins are clustered into 17 subfamilies, marked by various colors.