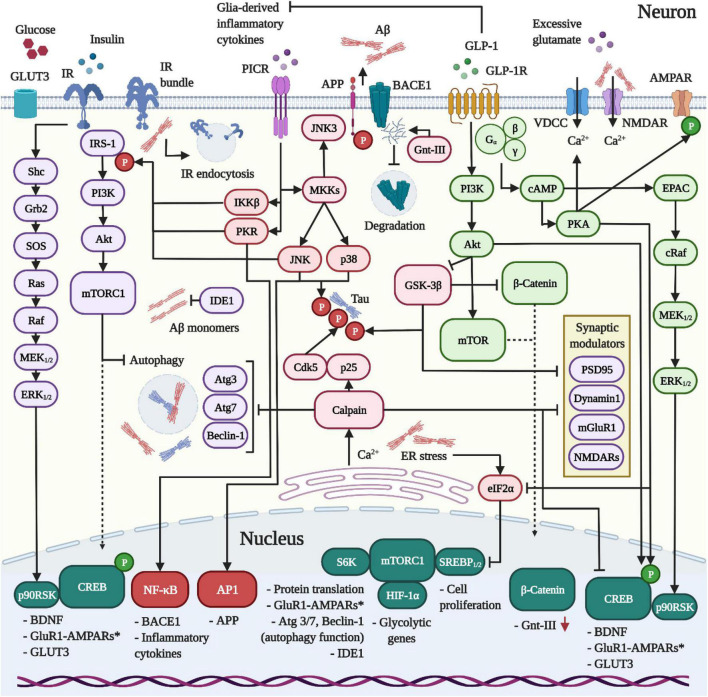
FIGURE 1.
Dynamics between IR, GLP-1R and PICR-signaling in neurons. 1 The release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the activation of PICRs on neurons induce the kinases IKKβ, PKR, and JNK to trigger the inhibitory Ser-phosphorylation of IRS-1 and neuronal insulin resistance in AD and PD. Aβ was further shown to drive IR clustering and endocytosis. In addition, Aβ provokes intracellular Ca2+ accumulation by external (VDCCs/NMDARs) and internal means (ER). The latter reinforces the desensitization of the insulin pathway, blocks protein translation (eIF2α/mTORC1 pathway) and activates the Ca2+-sensitive calpain to impair autophagy, interfere with the synaptic function and promote the hyperphosphorylation of Tau by cleaving p35 into the Cdk5-activating binding partner p25. Further consequences of inflammation and insulin resistance include reduced IDE1 expression, enhanced APP and BACE1 expression, Aβ overproduction and amassment, the loss of neuroprotective PI3K/Akt and CREB signaling, GSK-3β hyperactivity and concomitant Tau hyperphosphorylation. Crucially, the impairment of the Akt/mTor pathway following insulin resistance impedes the expression of glycolytic enzymes, thus enforcing bioenergetic impairments and glucose hypometabolism. 2 In contrast to the IR, the GLP-1R does not desensitize in neurons. When activated, the GLP-1R stimulates PI3K/Akt/mTORC1, cAMP/PKA, MEK/ERK, and CREB/BDNF-signaling to ameliorate the Aβ (section “GLP-1R agonists are neuroprotective and prevent amyloid beta accumulation in vivo”) and Tau (section “GLP-1R mimetics suppress Tau hyperphosphorylation and aggregation during AD”) pathologies through various mechanisms, suppress excessive Ca2+ influx and ER stress (not shown; details in sections “GLP-1 mimetics suppress Ca2+ deregulation by amyloid beta and excitotoxicity” and “GLP-1 analogues counteract endoplasmic reticulum stress”), restore insulin signaling (section “Insulin resistance and the neuronal energy metabolism”) by aiding the clearance of Aβ, normalize the autophagy function by raising the expression of autophagy modulators via mTORC1 (Atg3, Atg7, Beclin-1) (section “Autophagy and mitophagy”), elevate neurogenesis (section “GLP-1R agonists promote neurogenesis”) and promote the synaptic function, plasticity and memory (section “Pro-cognitive effects”). Importantly, the activation of GLP-1R on microglia and astrocytes induces the anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype and suppresses inflammatory cytokine production (not shown; see section Inflammation), thus preventing insulin resistance.