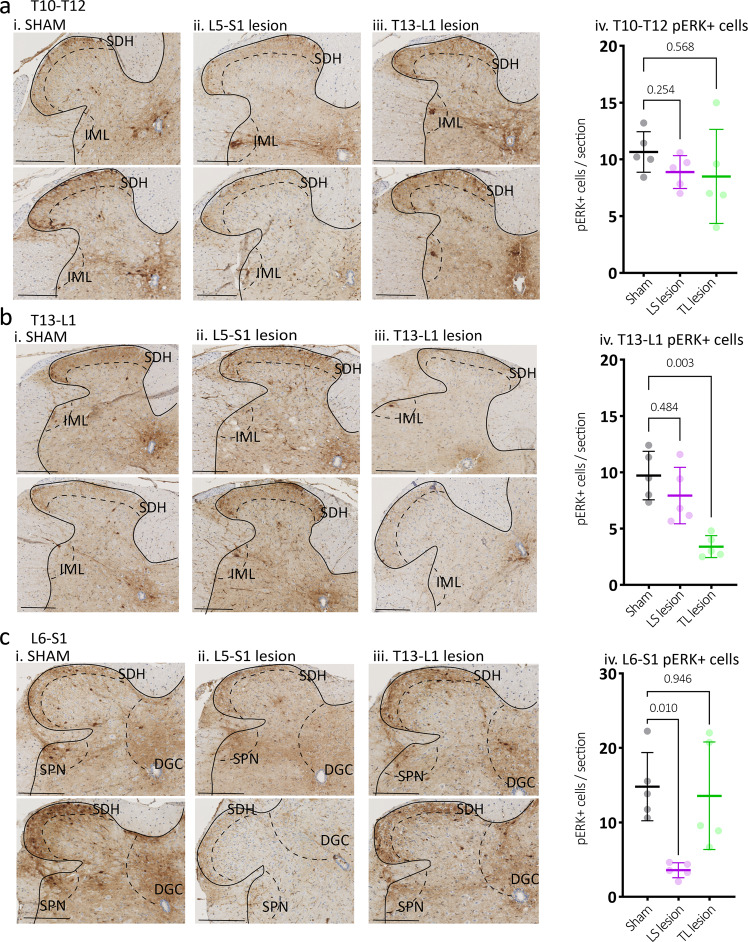
Fig. 7. Expression of cell activation marker pERK in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord following noxious colorectal distension.
Representative images of pERK-immunoreactive (-IR) (dark brown) nerve cell bodies, evoked by noxious in vivo colorectal distension in cross-sections of (a) T10–T12, (b) T13-L1, and (c) L6-S1 spinal cord dorsal horn from (i) Sham, (ii) LS lesion and (iii) TL lesion mice. Calibration, 100 µm. In sham mice, pERK-IR neurons were observed in the superficial dorsal horn laminae I and II (SDH) at all spinal levels and below this in the in deep dorsal horn lamina (LIII-IV) in the L6-S1 spinal cord. pERK-IR neurons were present in the dorsal grey commissure (DGC), in the intermediolateral nuclei (IML) in thoracic T10–T12 sections and in the sacral parasympathetic nuclei (SPN) in sacral sections. iv The number of pERK-IR neurons evoked by in vivo colorectal distension was quantified within sections of (a) T10–T12, (b) T13-L1, (c) L6-S1 spinal cord dorsal horn from sham (grey markers), TL lesion (green markers) and LS lesion mice (magenta markers). The mean number of pERK-IR neurons/section in the T10–T12 dorsal horn did not differ between experimental groups (N = 5 per group). However, they were significantly reduced in the (b) T13-L1 dorsal horn of TL lesion mice, and in the (c) L6-S1 dorsal horn in LS lesioned mice relative to sham controls. P values refer to two-way, repeated measures ANOVA, Tukey post-hoc comparison tests. Individual data points represent the mean number of pERK-IR neurons per section per mouse. All error bars represent mean ± SD, individual markers represent individual animal averages.