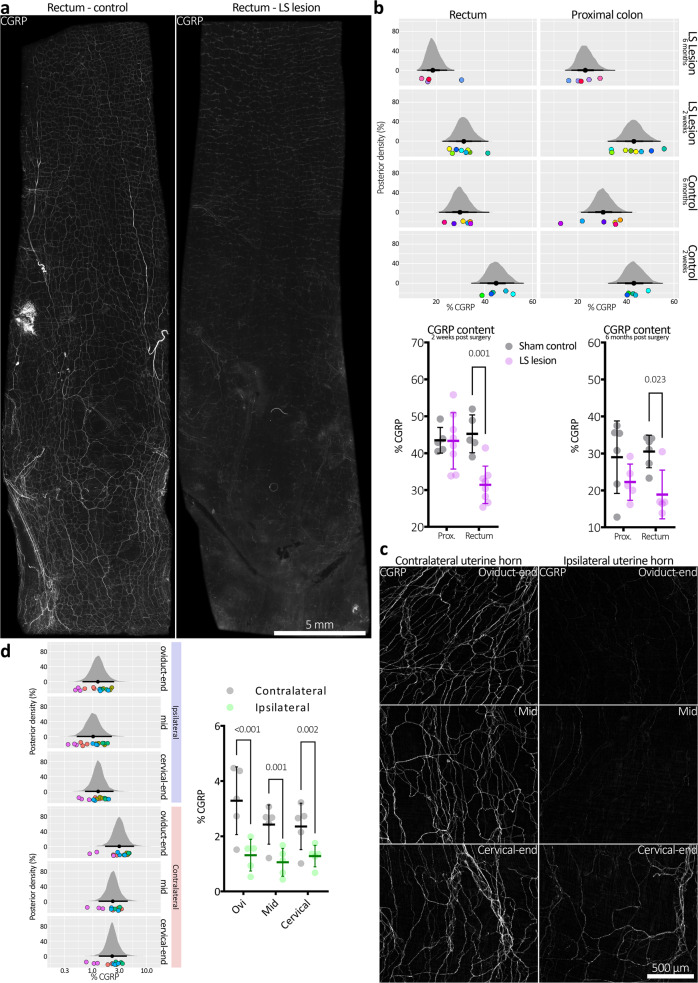
Fig. 9. Depletion of spinal afferent neuropeptide CGRP, after DRG removal.
a CGRP immunofluorescence in distal colons from control (sham) mice and from mice lacking bilateral L5-S1 DRG, both 2 weeks after surgery. Intensely CGRP-immunofluorescent axons are prominent in mouse colorectum, characteristic of spinal afferent nerves. Less intense CGRP immunofluorescence occurs in a subclass of enteric neuron. Whilst intense CGRP labelling was abolished by the LS lesion, CGRP was still detectable in enteric neurons. This is consistent with selective ablation of spinal afferent neurons from the colon in LS lesioned animals. b Summary of CGRP immunohistochemical results in both short (2-week post surgery) and long term (6 months post) mice. Here, posterior densities (vertical axis) represent probability distributions of the proportion CGRP immunoreactivity. The black dot below the centre of a distribution represents the mean and the horizontal black lines either side of the dot, from thickest to thinnest, represent the 50, 95 and 99.5% confidence intervals. CGRP immunoreactivity is quantified as the proportion (%) positive pixels per immunofluorescence micrograph. The results show significant reductions in CGRP immunofluorescence in the distal, but not proximal colon in both types of lesioned mice compared to their controls. This suggests the ablation of spinal afferent neurons is stable over long periods of time in the rectum. The spatial pattern of CGRP depletion is consistent with the known distribution of LS afferent neurons that enter the colorectum via pelvic/rectal nerve pathways. Coloured dots below the posterior densities represent individual animal averages. Identically coloured dots in horizontally adjacent graphs represent values from the same animal. The same data are presented below the panel of posterior densities as standard graphs, showing mean ± SD and individual markers for each animal average. c Representative micrographs showing CGRP immunofluorescence in uterine horn following unilateral removal of T13-L2 DRG. d Quantitative summary of CGRP immunofluorescence in the uterine horns. Ipsilateral CGRP density was significantly decreased relative to the contralateral horn in all subregions sampled. Posterior densities have the same definitions as described in (b) and coloured dots represent replicate measures (identical colours represent values from the same animal). The same data are also presented adjacent the panel of posterior densities as standard graphs, showing mean ± SD and individual markers for each animal average.