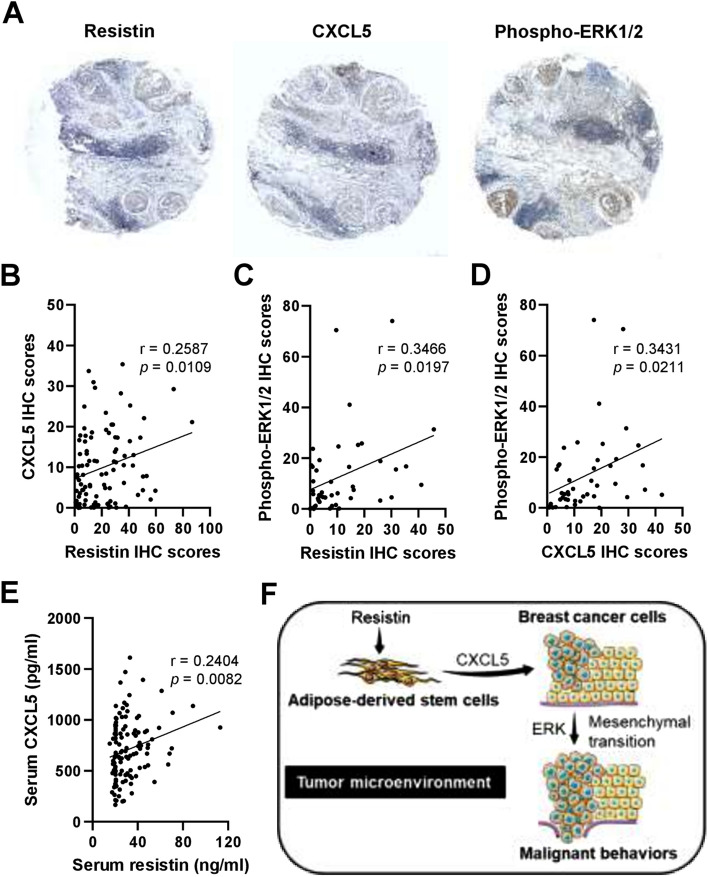
Figure 6.
Correlation analysis for the protein expression of resistin, CXCL5, and ERK phosphorylation in the tumor and serum specimens from breast cancer patients. (A) Representative images of immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining for resistin, CXCL5, and phospho-ERK1/2 expression in breast tumor sections from breast cancer patients. (B–D) The quantitative IHC scores were evaluated by HistoQuest software, followed by Pearson correlation (r) analysis between resistin and CXCL5 in (B) (n = 96), resistin and phospho-ERK1/2 in (C) (n = 45), and CXCL5 and phospho-ERK1/2 in (D) (n = 45). (E) The serum levels of resistin and CXCL5 in breast cancer patients were determined by ELISA, followed by Pearson correlation (r) analysis (n = 120). The mean ± SD of resistin and CXCL5 was 31.4 ± 15.4 ng/ml and 707.9 ± 293.4 pg/ml, respectively. (F) Schematic summary of the current study. Our preclinical and clinical data together suggest that CXCL5 may be secreted by resistin-stimulated ADSCs in the breast tumor microenvironment, promoting breast cancer cell malignancy via the participation of ERK pathway and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. The schematic summary in (F) was produced using the illustration elements from Servier Medical Art (https://smart.servier.com), which is in compliance with the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).