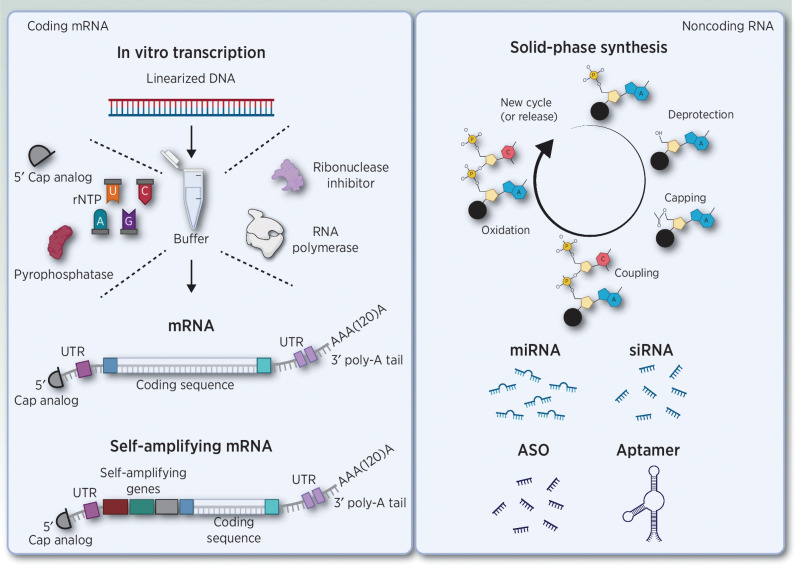
Figure 1.
Overview of coding and noncoding RNA structures. Left, in vitro transcription (iVT) of messenger RNA (mRNA). mRNA has several conserved features, including a 5′ cap structure, two extended untranslated regions (UTR) at the 5′ and 3′ end of the ORF, and a 3′ poly-A tail. The final iVT product can be mRNA or self-amplifying mRNA. Right, solid-phase synthesis of noncoding and antisense oligonucleotides. Abbreviations: ASO, antisense oligonucleotides; mRNA, messenger RNA; UTR, untranslated region; rNTP, ribonucleoside triphosphates; miRNA, microRNA; siRNA, small interfering RNA. Adapted from an image created with BioRender.com.