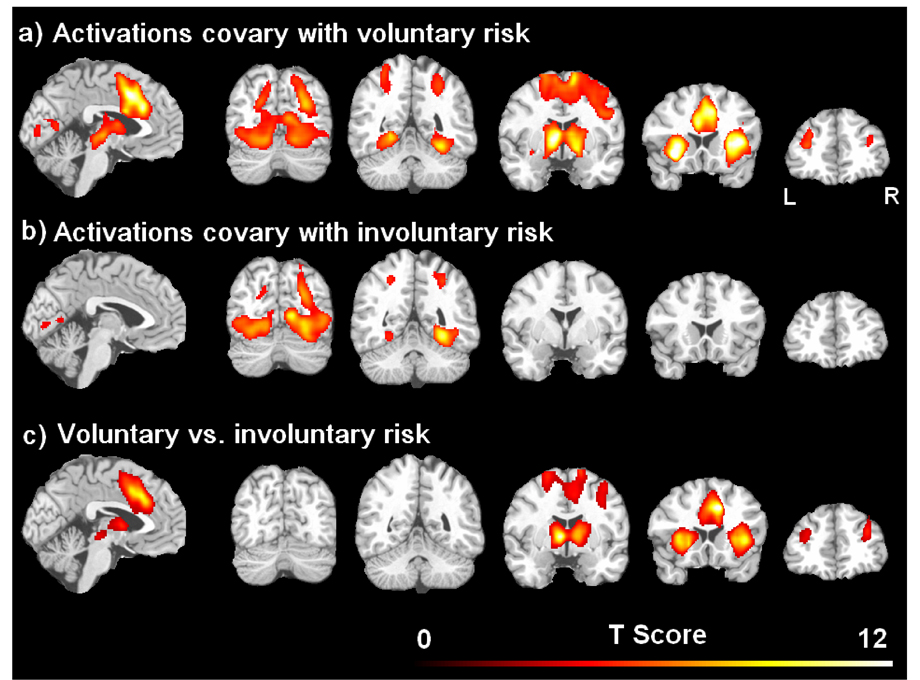
Figure 2.
Brain activations covaried with the parametric level of voluntary risk in the active choice task (a) and the parametric level of involuntary risk in the passive no-choice task (b), respectively. The brain activation difference between voluntary and involuntary risk were shown in (c). The threshold was set as the whole brain corrected p < 0.05.