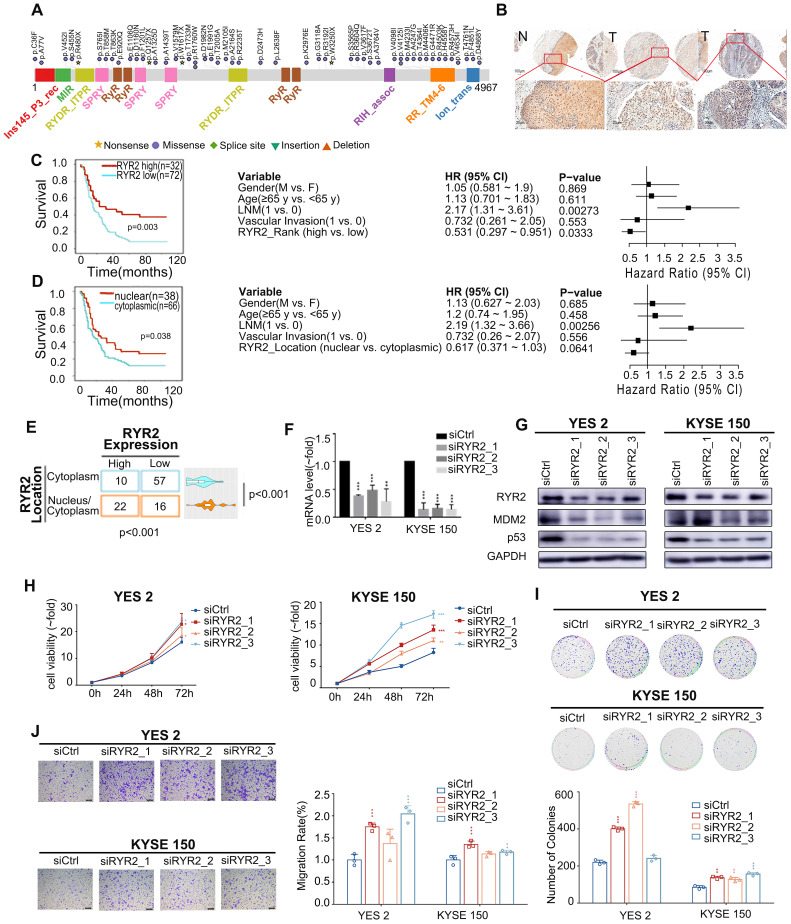
Figure 2.
Deficient RYR2 contributes to malignant phenotypes of ESCC. (A) A schematic representation of the domain structure of RYR2 shows the location of somatic variants identified in ESCC tumors. (B) Representative images of IHC for RYR2 in ESCC tissues and matched adjacent normal tissues. Scale bars, 200 µm. (C) Left: Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of patients with ESCC stratified by RYR2 expression (n = 104; p = 0.003, log-rank test). Right: Multivariate analysis of the hazard ratios (HR) showed that the downregulation of RYR2 was an independent prognostic factor for the overall survival (by the multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression model). The HR is presented as the means (95% confidence interval, 95% CI). (D) Left: Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of patients with ESCC stratified by RYR2 localization (n = 104; p = 0.038, log-rank test.) Right: Multivariate analysis of the hazard ratios (HR) showed that the translocation of RYR2 may be an independent prognostic factor for the overall survival rate (by the multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression model). The HR is presented as the means (95% confidence interval, 95% CI). (E) RYR2 expression and localization in normal and tumor tissue. (F) The mRNA levels of RYR2 in YES2 and KYSE150 cells after a knockdown by siRNAs. (G) The protein levels of RYR2, MDM2, and p53 in YES2 (left) and KYSE150 (right) cells after a knockdown by siRNAs. (H) MTS assay on YES2 and KYSE150 cells transfected with siRYR2 or siCtrl. (I) Colony formation assay on YES2and KYSE150 cells transfected with siRYR2 or siCtrl. Up: representative images. Down: statistical analysis. (J) Transwell assays on YES2 and KYSE150 cells transfected with siRYR2 or siCtrl. Left: representative images. Right: statistical analysis.