Figure 2. EVP cargo, biogenesis, and uptake.
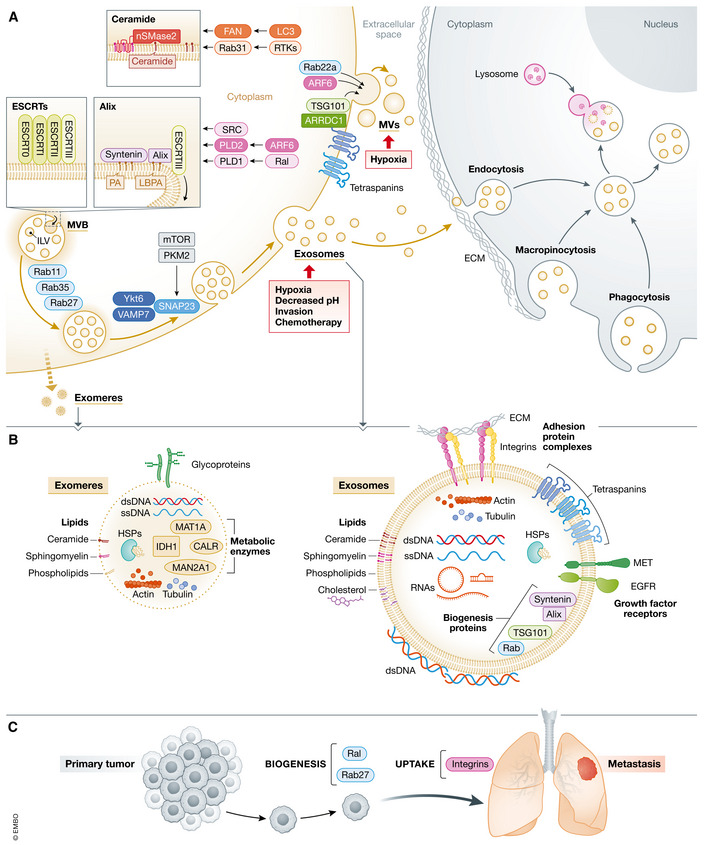
(A) EVP biogenesis occurs in MVB endosomes, giving rise to secreted exosomes, and at the plasma membrane, resulting in the generation of MVs, which are also termed ectosomes. Invagination of the endosome membrane leads to the formation of nanosized (50–150 nm) ILVs that are contained within the MVB lumen. ILV formation is regulated by various molecular processes at the MVB membrane that are each capable of capturing cargo and remodeling membranes for ILV generation and are also induced by upstream regulators. MVB trafficking is controlled by Rabs and SNARE‐complexes for secretion of exosomes at the cell surface. MVs/ectosomes range in size from 50 nm to almost 1 μm. Their budding occurs at plasma membrane microdomains enriched for ESCRT proteins, like TSG101, which is recruited by ARRDC1 for MV formation, and MV biogenesis is also stimulated by ARF6. In cancer, molecular pathways involving RTKs/Rab31, SRC, ARF6/PLD2, Ral/PLD1, and mTOR/PKM2 along with environmental and cellular factors related to hypoxia, pH, invasion, chemotherapy can all influence exosome biogenesis. Hypoxia and Rab22a promote MV formation in cancer cells. EVP uptake involves attachment of EVPs to extracellular matrix via adhesion molecules, such as integrins, on EVPs. Pathways of cellular uptake include endocytosis, macropinocytosis, and phagocytosis. Internalized EVPs traffic to the perinuclear area of recipient cells where they may fuse with lysosomes. (B) EVPs (including exomeres on the left and exosomes on the right) carry a variety of macromolecules, including proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. Transmembrane proteins include adhesion molecules, like integrins, growth factor receptors, and tetraspanins, which are involved in biogenesis and which may also mediate adhesion. Cytosolic proteins such as actin, HSPs and other biogenesis factors are also commonly found in EVPs. Both dsDNA and ssDNA are found associated with EVPs. Double‐stranded DNA is present both inside and on the surface of EVPs. Various RNAs, such as miRNAs, mRNAs, and other short and long noncoding RNAs, are carried by EVPs. Lipids, particularly cholesterol, phospholipids, ceramides, and sphingomyelin are enriched in EVPs. (C) Biogenesis and uptake factors functionally regulate in vivo cancer metastasis. Inhibition of Ral and Rab GTPases involved in biogenesis impairs metastasis. Blockade of exosomal integrins reduces exosome uptake and metastasis. HSP, heat shock protein; ILV, intralumenal vesicle; MVB, multivesicular body; MV, macrovesicle; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinases; dsDNA, double‐stranded DNA; ssDNA, single‐stranded DNA.
