Figure 6.
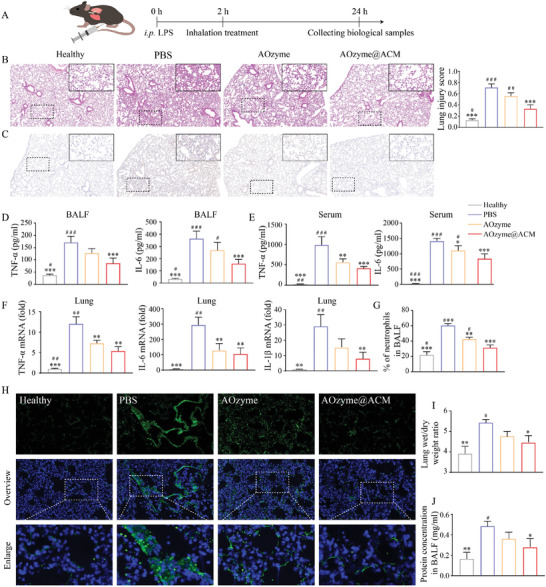
Pro‐efferocytic AOzyme@ACM alleviated sepsis‐related acute lung injury. A) Schematic depicting the animal study design. B) Histopathologic examination using H&E staining. C) Immunohistochemistry of TNF‐α expression within lung tissues. D) The level of TNF‐α and IL‐6 in BALF and E) serum were measured by ELISA. F) Detection of inflammatory cytokine mRNA (TNF‐α, IL‐6, and IL‐1β) expression in the lung tissues by RT‐qPCR. G) Neutrophil infiltration in BALF was analyzed by flow cytometry. H) Immunofluorescence staining of mice lung sections for ROS detection (DCFH‐DA, green) and DAPI (blue) in all groups. I) The wet/dry ratio of lung tissue and (J) total protein concentration in BALF were measured. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 5). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 versus PBS. # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, and ### p < 0.001 versus AOzyme@ACM (one‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test).
